The market situation for 2-FEA, a synthetic designer drug categorized as a research chemical, has been dynamic recently. 2-FEA, a derivative of amphetamine, has gained attention among buyers and sellers within the online vendor community.
Sellers offering 2-FEA have proliferated online, capitalizing on the demand from researchers seeking new compounds for experimentation. The substance is readily available for sale, often marketed as a research chemical with limited human consumption, bypassing legal restrictions.
Buyers, primarily research institutions and individual scientists, are drawn to 2-FEA due to its potential for novel pharmacological effects. Its emergence in the market has generated curiosity and interest among those studying psychoactive substances.
Despite its growing popularity, the legal status of 2-FEA remains to be determined in many jurisdictions, leading to a complex and evolving regulatory landscape. This ambiguity has prompted caution among sellers and buyers, as legal repercussions may vary by location.
- 1 Summary
- 2 Chemistry
- 3 Pharmacology
- 4 Subjective effects
- 5 Toxicity
- 6 Legal status
- 7 FAQ
- 7.1 1. What is 2-FEA?
- 7.2 2. Is 2-FEA legal?
- 7.3 3. How is 2-FEA typically used?
- 7.4 4. What are the effects of 2-FEA?
- 7.5 5. Is 2-FEA safe to use?
- 7.6 6. Are there any potential health risks associated with 2-FEA use?
- 7.7 7. Can 2-FEA lead to addiction?
- 7.8 8. What precautions should I take if considering 2-FEA use?
- 7.9 9. Are there any dangerous interactions with 2-FEA?
- 8 References
Summary
2-Fluoroethamphetamine (2-FEA) represents a novel stimulant within the amphetamine family, exhibiting typical stimulant attributes, including heightened alertness, improved concentration, and euphoria upon ingestion.
The precise effects of 2-FEA must be comprehensively documented among its user base, though anecdotal accounts hint at relatively mild stimulatory properties and potential serotonergic characteristics.
In the contemporary landscape, 2-FEA is readily available on online platforms specializing in research chemicals. It is strongly recommended that individuals exercise harm-reduction strategies when considering using this compound.
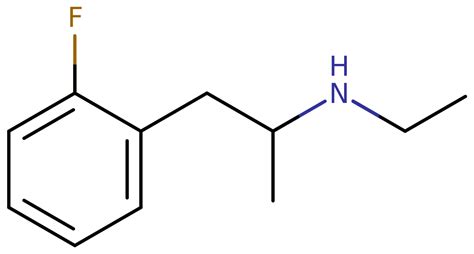
Chemistry
2-Fluoroethamphetamine (2-FEA) is a synthesized compound from the substituted amphetamine family. In this chemical group, molecules possess a phenethylamine foundation, characterized by a phenyl ring connected to an amino (NH2) group through an ethyl chain, along with an additional methyl substitution at the alpha position (Rα), thus designating them as alpha-methylated phenethylamines. Notably, 2-FEA incorporates an ethyl group attached to the terminal amine RN of the amphetamine core.
2-FEA serves as the N-ethylated counterpart to 2-FA (2-fluoroamphetamine).
Pharmacology
The comprehensive scientific exploration of 2-FEA has not paralleled that of conventional amphetamines. It is hypothesized that its primary mode of action involves functioning as a triple reuptake inhibitor and facilitating the release of crucial neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. 2-FEA is believed to exert its effects by acting as a neurotransmitter release agent and potentially by binding to and partially inhibiting the transporter proteins responsible for clearing substances from the synaptic cleft once they have transmitted neural impulses.

Subjective effects
The effects of 2-FEA are notably subtle and challenging to characterize comprehensively. Some user accounts describe it as relatively mild with minimal side effects, akin to 2-FA. However, others have reported heightened physical side effects or serotonergic activity reminiscent of 3-FEA.
Disclaimer: The following effects are drawn from the Subjective Effect Index (SEI), a collection of anecdotal user reports and personal analyses contributed by PsychonautWiki contributors. As such, they should be approached with a measure of scepticism.
It’s important to note that these effects may not consistently manifest, and their occurrence is not always predictable or reliable. Higher doses are more likely to encompass the full range of products, but they also increase the risk of adverse outcomes, including addiction, severe injury, or even death ☠.
Physical:
- Stimulation and Sedation: 2-FEA may paradoxically induce both sedating and stimulating effects, with serotonin release possibly contributing to the sedating aspects. The stimulating effects are typically more pronounced at doses within or exceeding the substantial range and often emerge after the peak effects wane.
- Physical Euphoria
- Tactile Enhancement
- Enhanced Stamina
- Abnormal Heartbeat (citation needed)
- Increased Heart Rate (citation needed)
- Elevated Blood Pressure (citation needed)
- Appetite Suppression
- Bronchodilation
- Dehydration
- Dry Mouth
- Frequent Urination
- Increased Body Temperature
- Profuse Sweating
- Nausea
- Pupil Dilation
- Teeth Grinding
- Temporary Erectile Dysfunction
- Vasoconstriction
- Restless Legs
Visual:
- Visual effects are typically less consistent and become more noticeable at higher doses. They resemble deliriant experiences and are more likely to manifest in dimly lit environments.
- Distortions
- Drifting (Breathing and Morphing): Typically subtle and only evident at higher doses or when combined with cannabis.
- Brightness Alteration: 2-FEA can enhance brightness perception due to its pupil-dilating effects.
- Hallucinatory States
- Transformations: Occurs rarely, primarily at high doses, during the comedown, or after prolonged wakefulness. It tends to be mild when it does manifest.
Cognitive:
- The mental effects of 2-FEA are generally understated, featuring mild to moderate stimulation.
- Analysis Enhancement
- Anxiety & Paranoia: Typically associated with excessive doses or redosing, especially after prolonged wakefulness.
- Cognitive Euphoria
- Compulsive Redosing
- Delusion
- Disinhibition
- Ego Inflation
- Emotion Suppression
- Focus Enhancement
- Increased Libido
- Augmented Music Appreciation
- Motivation Enhancement
- Improved Bodily Control
- Thought Acceleration
- Thought Organization
- Heightened Wakefulness
- Time Distortion: Often experienced as a sense of time passing more swiftly than usual.
After:
- The offset of a 2-FEA stimulant experience is often marked by adverse and uncomfortable effects, commonly called a “comedown.” These sensations arise due to neurotransmitter depletion and may include:
- Anxiety
- Cognitive Fatigue
- Delusion
- Depersonalization
- Depression
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Suppressed Motivation
- Psychosis
- Thought Deceleration
- Prolonged Wakefulness
Toxicity
The toxicity and potential long-term health consequences associated with the recreational use of 2-FEA have not been subjected to comprehensive scientific investigation, primarily due to its limited history of human consumption. As such, the exact toxic dosage remains unknown.
Anecdotal reports from individuals who have experimented with 2-FEA suggest that no immediate adverse health effects appear to be linked to its cautious use at low to moderate doses or infrequent consumption. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that complete safety cannot be guaranteed.
It is strongly advised that individuals employ harm reduction practices when considering the use of this substance.
Tolerance and Addiction Potential:
Like other stimulants, chronic use of 2-FEA can lead to moderate addiction potential and a high risk of abuse. Some users may develop psychological dependence, and discontinuing use may result in cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Tolerance often develops with repeated and prolonged 2-FEA use, necessitating higher doses to achieve the same effects. It typically takes 3 to 7 days for tolerance to decrease by half and 1 to 2 weeks to return to baseline if further consumption is avoided. It’s noteworthy that 2-FEA exhibits cross-tolerance with all dopaminergic stimulants, meaning that the effects of other stimulants will be diminished after 2-FEA consumption.
Dangerous Interactions:
Caution is essential when combining psychoactive substances, as certain combinations can pose serious health risks. It is imperative to conduct independent research to ensure the safety of such combinations. Here are some known dangerous interactions, although this list may not be exhaustive:
- Stimulants: Combining 2-FEA with other stimulants can elevate heart rate and blood pressure to hazardous levels.
- 25x-NBOMe & 25x-NBOH: These compounds are highly stimulating and physically taxing. Mixing them with 2-FEA should be strictly avoided due to the risk of excessive stimulation, heart strain, increased blood pressure, panic attacks, thought loops, seizures, and potentially heart failure.
- Alcohol: Combining alcohol with stimulants can be dangerous, as stimulants can mask alcohol’s depressant effects. This can lead to over-intoxication, blackouts, and severe respiratory depression.
- DXM: Combining DXM with 2-FEA should be avoided due to its inhibitory effects on serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake, which can increase the risk of panic attacks and hypertensive crises.
- MDMA: Combining MDMA with 2-FEA may intensify neurotoxic effects and pose risks related to elevated blood pressure and heart strain (cardiotoxicity).
- MXE: Reports suggest that mixing MXE with 2-FEA may significantly increase blood pressure and the risk of mania and psychosis.
- Dissociatives: Combining 2-FEA with dissociatives can amplify the risk of delusions, mania, and psychosis.
- Tramadol: Tramadol’s seizure threshold-lowering effects may be exacerbated when combined with stimulants like 2-FEA.
- MAOIs: This combination may dangerously elevate neurotransmitter levels, potentially leading to severe or fatal consequences.
- Cocaine: Combining cocaine with 2-FEA may increase strain on the heart and should be avoided.
Always exercise extreme caution when considering the simultaneous use of substances, as the risks can be severe and life-threatening.
Legal status
Currently, 2-FEA resides in a legal grey area worldwide, lacking specific legal categorization as an illegal or “scheduled” substance in most countries. However, it’s important to note that individuals may still face legal consequences for their possession under specific circumstances, such as invoking analogue laws or demonstrating intent to sell or consume.
Here is the legal status of 2-FEA in several countries:
- Canada: 2-FEA would be classified as Schedule I due to its analogical relationship with Amphetamine.
- Germany: Since November 26, 2016, 2-FEA falls under the New Psychoactive Substances Act (NpSG) regulation. Production and import with the intent to market, as well as administering to others and trading, are punishable offences. While possession is considered illegal, it is not penalized.
- New Zealand: In New Zealand, 2-FEA is regarded as an amphetamine analogue and is thus categorized as a Schedule 3 controlled substance.
- Switzerland: 2-FEA can be classified as a controlled substance as a specified derivative of alpha-methylphenethylamine, as per Verzeichnis E point 130. It is legal when utilized for scientific or industrial purposes.
- United Kingdom: Under the amphetamine analogue clause of the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971, 2-FEA is classified as a Class A drug in the United Kingdom.
Individuals need to stay informed about the legal status of 2-FEA within their respective jurisdictions, as regulations may evolve, potentially impacting its legality and consequences related to its possession or use.
FAQ
1. What is 2-FEA?
- 2-FEA, or 2-Fluoroethamphetamine, is a synthetic compound in the substituted amphetamine class. It shares structural similarities with amphetamine and is known for its stimulant effects.
2. Is 2-FEA legal?
- The legal status of 2-FEA varies by country. It is considered a controlled substance in some places and is unregulated in others. It’s essential to check the specific laws in your jurisdiction before obtaining or using 2-FEA.
3. How is 2-FEA typically used?
- 2-FEA is typically consumed orally and is available in various forms, including capsules, powder, or tablets. Users should follow dosing guidelines carefully if choosing to use it.
4. What are the effects of 2-FEA?
- The effects of 2-FEA can include stimulation, enhanced focus, euphoria, and mild hallucinatory experiences at higher doses. However, its results can vary from person to person, and it is essential to exercise caution due to its limited research.
5. Is 2-FEA safe to use?
- The safety of 2-FEA needs to be well-established due to limited scientific research. Users should be aware of potential risks and employ harm-reduction practices. It is advisable to start with lower doses and avoid mixing it with other substances.
6. Are there any potential health risks associated with 2-FEA use?
- Like many stimulants, 2-FEA use may be associated with health risks, including cardiovascular issues, addiction, and psychological side effects. Long-term effects and toxicity are not well-documented.
7. Can 2-FEA lead to addiction?
- Yes, like other stimulants, 2-FEA has the potential for psychological dependence and addiction, especially with chronic or high-dose use. Users should be aware of this risk.
8. What precautions should I take if considering 2-FEA use?
- It is strongly recommended to exercise harm reduction practices, which include starting with a low dose, avoiding frequent use, staying hydrated, and being cautious about potential interactions with other substances.
9. Are there any dangerous interactions with 2-FEA?
- Yes, 2-FEA can have dangerous interactions with other substances, especially stimulants and depressants. Combining it with certain substances can lead to serious health risks, including cardiovascular issues.
References
- Tessel, R. E., Woods, J. H. (May 1978). “Substituted N-ethylamphetamine self-injection responding in the rhesus monkey: structure-activity relationships”. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 205 (2): 274–281. ISSN 0022-3565.
- Talaie, H.; Panahandeh, R.; Fayaznouri, M. R.; Asadi, Z.; Abdollahi, M. (2009). “Dose-independent occurrence of seizure with tramadol”. Journal of Medical Toxicology. 5 (2): 63–67. doi:10.1007/BF03161089. eISSN 1937-6995. ISSN 1556-9039. OCLC 163567183.
- Gillman, P. K. (2005). “Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, opioid analgesics and serotonin toxicity”. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 95 (4): 434–441. doi:10.1093/bja/aei210 Freely accessible. eISSN 1471-6771. ISSN 0007-0912. OCLC 01537271. PMID 16051647.
- Branch, L. S. (2022), Consolidated federal laws of Canada, Controlled Drugs and Substances Act
- “Anlage NpSG” (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
- “Gesetz zur Bekämpfung der Verbreitung neuer psychoaktiver Stoffe” (PDF) (in German). Bundesanzeiger Verlag. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
- “§ 4 NpSG” (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
- Misuse of Drugs Act 1975 No 116 (as of 01 July 2022), Public Act – New Zealand Legislation
- “Verordnung des EDI über die Verzeichnisse der Betäubungsmittel, psychotropen Stoffe, Vorläuferstoffe und Hilfschemikalien” (in German). Bundeskanzlei [Federal Chancellery of Switzerland]. Retrieved January 1, 2020.
- Misuse of Drugs Act 1971

Leave a Reply