Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
- 1 Summary
- 2 Legal status
- 3 FAQ
- 3.1 1. What is Nitracaine?
- 3.2 2. How is Nitracaine chemically structured?
- 3.3 3. What are the potential effects of Nitracaine?
- 3.4 4. Is Nitracaine considered a hazardous substance?
- 3.5 5. What is the relationship between Nitracaine and dimethocaine?
- 3.6 6. Is Nitracaine legal to use and possess?
- 3.7 7. What are the potential risks and side effects of Nitracaine use?
- 3.8 8. Can Nitracaine be used for medical purposes?
- 4 References
Summary
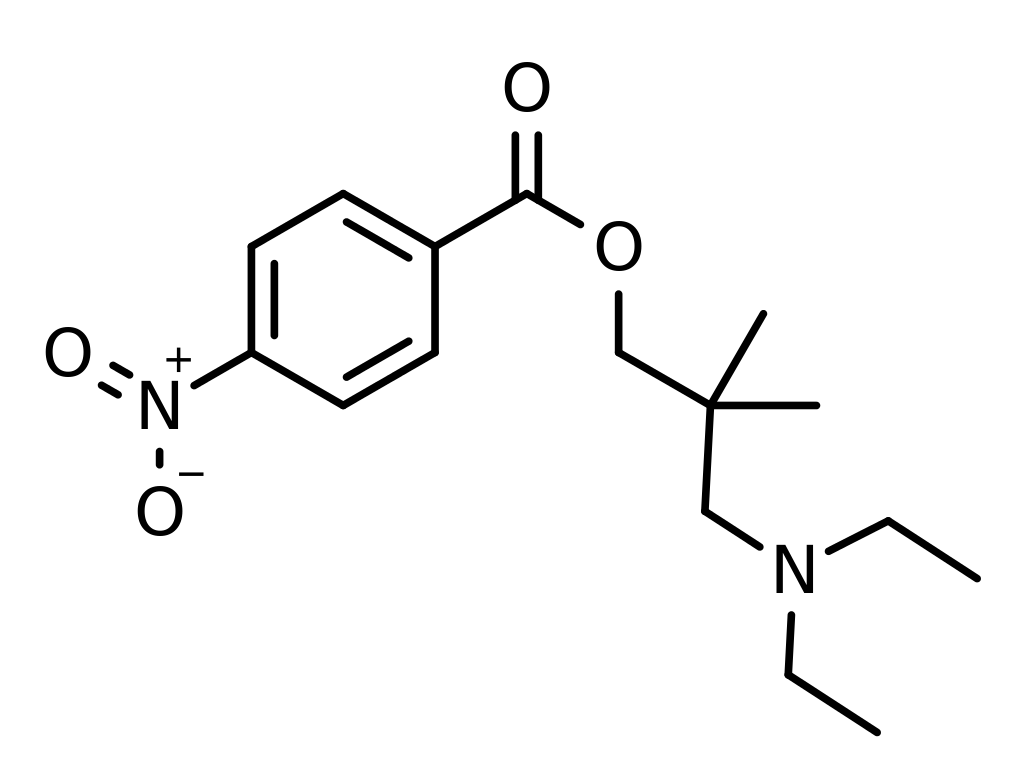
Nitracaine is a synthetic compound categorized as a local anaesthetic with stimulant attributes. It falls within the drug classification of local anaesthetics and exhibits a chemical connection to cocaine. Although Nitracaine shares specific effects reminiscent of cocaine, it possesses its unique pharmacological profile. Structurally, Nitracaine comprises a benzoic acid ester and a para-substituted phenyl ring. Formally identified as 3-(diethylamino)-2,2-dimethylpropyl 4-nitrobenzoate, its anaesthetic properties stem from the presence of the nitro group (NO2) within its molecular makeup.
Furthermore, Nitracaine demonstrates a close chemical relationship with dimethocaine.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 1648893-21-3 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 91936940 |
| ChemSpider | 29341792 |
| UNII | B8ZB08WI9O |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H24N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 308.378 g·mol−1 |
Legal status
On September 25, 2019, Sweden’s public health agency proposed the categorization of Nitracaine as a potentially dangerous substance.
FAQ
1. What is Nitracaine?
- Nitracaine is a synthetic compound classified as a local anaesthetic with stimulant properties. It shares chemical similarities with cocaine but has its distinct pharmacological profile.
2. How is Nitracaine chemically structured?
- Nitracaine has a chemical structure characterized by a benzoic acid ester combined with a para-substituted phenyl ring. Its formal chemical name is 3-(diethylamino)-2,2-dimethylpropyl 4-nitrobenzoate. The presence of the nitro group (NO2) in its molecular structure contributes to its anaesthetic properties.
3. What are the potential effects of Nitracaine?
- Nitracaine is known to have stimulant properties, similar to cocaine. However, its specific effects and potency may vary among individuals. It may induce feelings of alertness, increased energy, and euphoria.
4. Is Nitracaine considered a hazardous substance?
- In some jurisdictions, including Sweden, Nitracaine has been suggested for classification as a potentially hazardous substance by public health authorities. This designation is due to safety concerns and potential risks associated with its use.
5. What is the relationship between Nitracaine and dimethocaine?
- Nitracaine is closely related to dimethocaine, another synthetic compound with similar effects. Both substances are sometimes used recreationally and share chemical features, although they may have distinct properties and effects.
6. Is Nitracaine legal to use and possess?
- The legal status of Nitracaine varies by country and region. It is essential to check local laws and regulations regarding this substance’s possession, sale, or use, as it may be subject to legal restrictions.
7. What are the potential risks and side effects of Nitracaine use?
- Nitracaine use may be associated with various health risks and side effects, including cardiovascular issues, nervous system disturbances, and addiction potential. The specific risks can vary depending on dosage, frequency of use, and individual susceptibility.
8. Can Nitracaine be used for medical purposes?
- Nitracaine is not approved for medical use and is primarily encountered in recreational or non-medical contexts. It is essential to rely on medically approved substances for legitimate medical needs.
References
- In January 2014, Power JD, Scott KR, Gardner EA, Curran McAteer BM, O’Brien JE, Brehon M, Talbot B, Kavanagh PV conducted research on the syntheses, characterization, and in vitro metabolism of nitracaine, methoxypiperamide, and mephtetramine. Their findings were published in “Drug Testing and Analysis,” Volume 6 (7–8), pages 668–75. The research can be accessed via DOI: 10.1002/dta.1616, and the PMID is 24574100.
- In March 2014, W. Joe Acton, Matteo Lanza, Bishu Agarwal, Simone Jürschik, Philipp Sulzer, Kostiantyn Breiev, Alfons Jordan, Eugen Hartungen, Gernot Hanel, Lukas Märk, Chris A. Mayhew, and Tilmann D. Märka conducted headspace analysis of new psychoactive substances using a Selective Reagent Ionisation-Time of Flight-Mass Spectrometer. Their work was published in the “International Journal of Mass Spectrometry,” Volume 360, pages 28–38. This research can be found under DOI: 10.1016/j.ijms.2013.12.009, and it’s available via PMC: PMC 4375562, with a PMID of 25844048.
- Information about Nitracaine can be found in the “New Synthetic Drugs Database.”
- On September 25, 2019, the Swedish public health authority, Folkhälsomyndigheten, proposed the classification of thirteen substances as narcotics or hazardous goods, which included Nitracaine. This announcement was made in Swedish and can be accessed via the source “Tretton ämnen föreslås klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara.”