Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
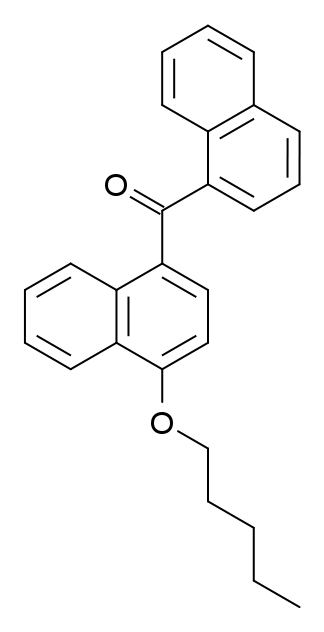
CB-13, also known as CRA13 and SAB-378, is a cannabinoid pharmaceutical compound. This substance is a robust agonist for CB1 and CB2 receptors, yet it cannot breach the blood-brain barrier. Consequently, at lower doses, CB-13 primarily elicits peripheral effects, while indications of central effects, such as catalepsy, manifest only when administered at significantly higher doses. Notably, CB-13 has demonstrated antihyperalgesic properties in animal research, and it has advanced to the initial stages of human clinical trials.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 432047-72-8 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 9799417 |
| ChemSpider | 7975182 |
| UNII | 9XRJ6055XT |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL244403 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID60430920 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H24O2 |
| Molar mass | 368.476 g·mol−1 |
Legal Status
In October 2015, CB-13 was classified as a regulated substance in China.
North Dakota designates CB-13 as a Schedule I controlled substance.
FAQ
1. What is CB-13?
- CB-13 is a synthetic cannabinoid compound known for its activity on the endocannabinoid system, particularly as an agonist for CB1 and CB2 receptors.
2. Is CB-13 Legal?
- The legal status of CB-13 varies by country and state. It’s essential to check your local regulations. As of my last update in 2025, it was classified as a controlled substance in China and a Schedule I controlled substance in North Dakota.
3. What Are the Effects of CB-13?
- CB-13 is reported to produce both peripheral and central effects. At lower doses, it primarily exhibits peripheral effects, while higher doses may lead to central effects like catalepsy.
4. Is CB-13 Safe?
- The safety of CB-13 is a subject of ongoing research. Like other synthetic cannabinoids, it may have unpredictable and potentially harmful effects. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional and use it cautiously.
5. What Are the Potential Medical Uses of CB-13?
- CB-13 has demonstrated antihyperalgesic properties in animal studies, suggesting its potential as a pain management option. It has also progressed to preliminary human trials, but further research is needed.
6. How Can I Obtain CB-13 for Research or Medical Purposes?
- Access to CB-13 for research or medical purposes is subject to strict regulations. Researchers and healthcare professionals must follow local laws and regulations regarding the acquisition and use of CB-13.
7. Are There Any Known Side Effects of CB-13?
- While side effects may vary, potential side effects of CB-13 could include nausea, dizziness, and central nervous system effects at higher doses. However, more research is needed to understand its side effect profile fully.
8. Is CB-13 the Same as Cannabis or Cannabidiol (CBD)?
- No, CB-13 is a synthetic compound designed to interact with cannabinoid receptors. It differs from natural cannabis and CBD, which are plant-derived compounds with distinct properties.
9. Can CB-13 Cause Addiction?
- Like many substances that affect the endocannabinoid system, CB-13 may have addictive potential, but more research is required to determine the extent of this risk.
10. Where Can I Find More Information About CB-13?
- Stay informed through reputable sources, scientific journals, and regulatory agencies that provide updates on CB-13, its legal status, and its potential applications. Always consult with experts in the field for the latest information and guidance.
References
- Cluny NL, Keenan CM, Duncan M, Fox A, Lutz B, Sharkey KA (September 2010). “SAB378: Unveiling a Peripherally Restricted Cannabinoid CB1/CB2 Receptor Agonist’s Impact on Gastrointestinal Motility and Experimental Colitis in Mice.” Published in The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 334(3), 973–980. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.169946. PMID: 20571060. S2CID 9198992.
- Dziadulewicz EK, Bevan SJ, Brain CT, Coote PR, Culshaw AJ, Davis AJ, et al. (August 2007). “Naphthalen-1-yl-(4-pentyloxynaphthalen-1-yl)methanone: A Potent, Orally Bioavailable Human CB1/CB2 Dual Agonist with Antihyperalgesic Properties and Restricted Central Nervous System Penetration.” Featured in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 50(16), 3851–3856. doi:10.1021/jm070317a. PMID: 17630726.
- Gardin A, Kucher K, Kiese B, Appel-Dingemanse S (April 2009). “CB-13: A Novel Cannabinoid Agonist – First Insights into Human Pharmacokinetics and Safety.” Presented in Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 37(4), 827–833. doi:10.1124/dmd.108.024000. PMID: 19144772. S2CID 15150118.
- “关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知” [Notice on Printing and Distributing the “Measures for the Scheduling of Non-Pharmaceutical Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances”] (in Chinese). Issued by the China Food and Drug Administration on September 27, 2015. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015. Retrieved on October 1, 2015.
- “Schedule 1” (PDF). Official document from the Sixty-eighth Legislative Assembly of North Dakota, dated January 3, 2023.