Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
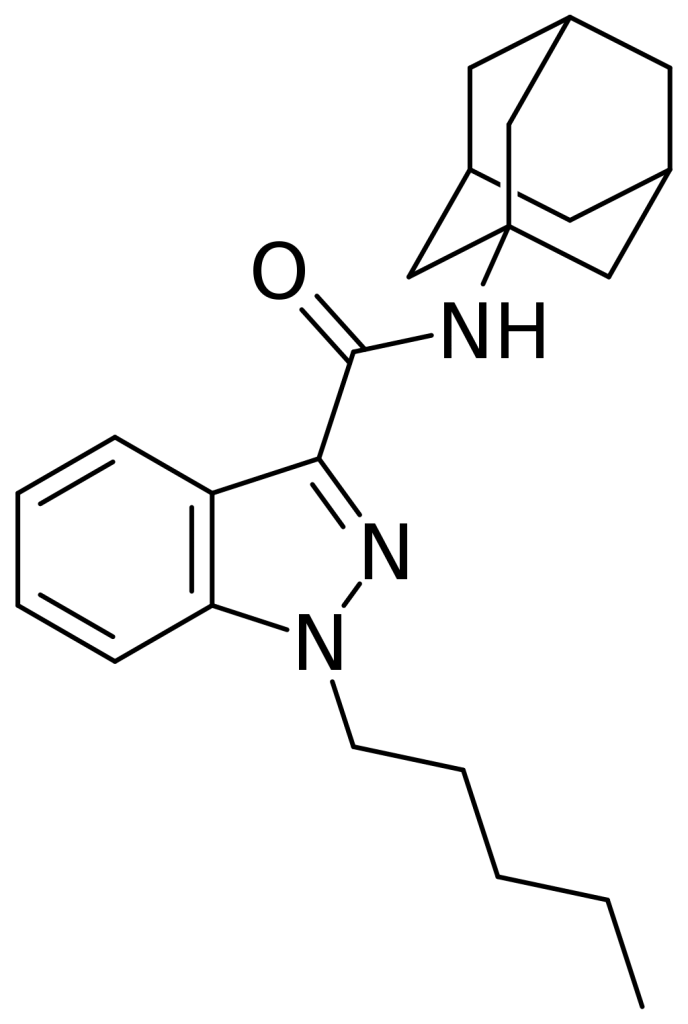
APINACA, also known as AKB48 or N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide, is a substance that functions as a reasonably potent agonist for cannabinoid receptors. It exhibits full agonist activity at the CB1 receptor, with an EC50 of 142 nM and a Ki of 3.24 nM. To provide context, this Ki value is notably lower than that of Δ9-THC (28.35 nM) and JWH-018 (9.62 nM).
At the CB2 receptor, APINACA functions as a partial agonist, with an EC50 of 141 nM and a Ki of 1.68 nM. These values can be compared to those of Δ9-THC (37.82 nM) and JWH-018 (8.55 nM). The pharmacological profile of APINACA is further described in a discontinued patent application.
This compound had yet to be previously documented in scientific or patent literature. It was initially detected in laboratories in Japan in March 2012, where it was identified as an ingredient in synthetic cannabis smoking blends. APINACA was found in conjunction with a related compound called APICA.
Structurally, APINACA bears a strong resemblance to cannabinoid compounds outlined in a patent from the University of Connecticut. It features a straightforward pentyl chain at the indazole 1-position. Despite not being explicitly disclosed as an example in the patent, APINACA falls within the patent’s claims.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 1345973-53-6 (1-adamantyl isomer) 1400742-54-2 (2-adamantyl isomer) |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 57404063 |
| ChemSpider | 28189076 |
| UNII | MHR0400Y84 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID90928683 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H31N3O |
| Molar mass | 365.521 g·mol−1 |
Legality
APINACA faced legal restrictions in various countries, including Japan in 2012, New Zealand with a temporary ban starting from 13 July 2012, and Latvia since 14 November 2013.
In the United States, APINACA has been classified as a Schedule I controlled substance since 2013, and it is also prohibited in Germany as an Anlage II controlled drug.
Singapore listed APINACA in the Fifth Schedule of the Misuse of Drugs Act (MDA), making it illegal as of May 2015. Furthermore, as of October 2015, China categorized APINACA as a controlled substance. The Czech Republic also imposed a ban on APINACA.
FAQ
- What is APINACA?
- APINACA, also known as AKB48, is a synthetic drug that acts as an agonist for cannabinoid receptors. It has an affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors, making it similar to cannabinoids found in cannabis.
- Is APINACA legal?
- The legal status of APINACA varies from country to country. It has been banned in several nations, including Japan, New Zealand, Latvia, the United States, Germany, Singapore, China, and the Czech Republic. It is considered a controlled substance in these regions.
- How is APINACA detected?
- A forensic standard of APINACA is available for use in detecting the presence of the compound. Additionally, APINACA is included on the Forendex website, a resource for identifying potential drugs of abuse.
- What are the effects of APINACA use?
- APINACA’s effects are similar to those of other synthetic cannabinoids, and they can include altered perception, relaxation, and potential adverse reactions such as anxiety, paranoia, and rapid heartbeat. However, the specific effects may vary from person to person.
- Why was APINACA banned in multiple countries?
- APINACA was banned due to concerns about its safety and potential health risks. Its classification as a controlled substance was often based on evidence of its psychoactive effects and the potential for abuse.
- Is APINACA the same as natural cannabis?
- No, APINACA is a synthetic compound designed to mimic the effects of natural cannabis. While it interacts with the same receptors as cannabis, its chemical structure and effects can be different and, in some cases, more potent.
- What should I do if I suspect someone is using APINACA?
- If you suspect someone is using APINACA or any other potentially harmful substance, it’s important to seek help or support. Encourage the individual to contact a healthcare professional or substance abuse counselor for guidance and assistance.
- Are there any potential health risks associated with APINACA use?
- Yes, like other synthetic cannabinoids, APINACA can pose health risks. These risks may include anxiety, hallucinations, increased heart rate, and, in some cases, severe adverse reactions. Its use can be unpredictable and should be avoided.
- Where can I find more information about APINACA?
- To learn more about APINACA, you can consult reliable sources such as government health agencies, substance abuse treatment centers, or medical professionals who can provide information on its effects, risks, and legal status in your region.
References
- Regulation in BrazilIn Brazil, the use of substances like APINACA is regulated by the “RDC Nº 804 – Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial” issued by the Collegiate Board. This resolution outlines the control of narcotic, psychotropic, precursor, and other substances.
- Early Detection in Synthetic ProductsAPINACA was initially identified in illegal products by laboratories in Japan in March 2012, along with related compounds like APICA. These synthetic cannabinoids have been known to appear in the composition of synthetic cannabis smoking blends.
- Scientific ResearchExtensive research has been conducted to understand the pharmacological properties and effects of APINACA. Studies have explored its impact on the “tetrad,” sensorimotor, neurological, and neurochemical responses in mice, both in vitro and in vivo.
- Chemical IdentificationAPINACA belongs to the group of azaindole-adamantyl-derived synthetic cannabinoids. It is distinguishable by its chemical structure, particularly its adamantyl-derived core.
- International Legal StatusThe legal status of APINACA varies across different countries. For instance, it was banned in Japan in 2012 and designated as a temporary class drug in New Zealand from July 13, 2012. It has been classified as a controlled substance in the United States since 2013.
- Global EnforcementAPINACA is subject to regulation in several other countries, including China, Germany, Singapore, and the Czech Republic. Each nation has its specific regulations and control measures in place.
- Forensic Standards and DetectionForensic standards for detecting APINACA are available for law enforcement and investigative purposes. Additionally, APINACA is included in the Forendex website as a potential drug of abuse for identification and monitoring.