Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
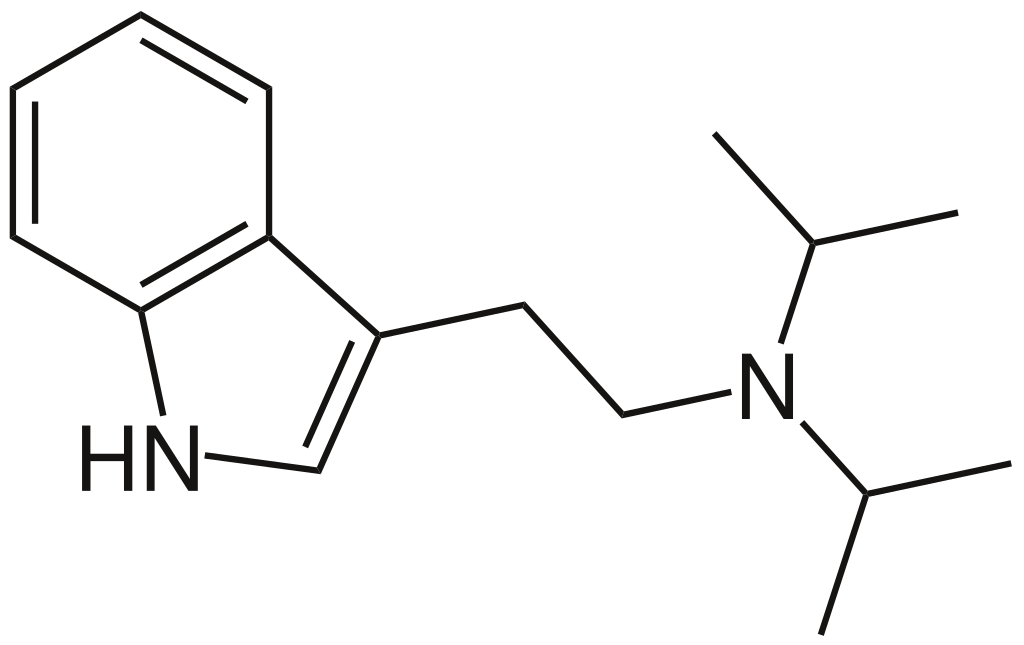
Diisopropyltryptamine, often abbreviated as DiPT and also referred to as N, N-diisopropyltryptamine, is a member of the tryptamine family known for its psychedelic and hallucinogenic properties. What sets DiPT apart from many other hallucinogens is its distinctive effect: instead of predominantly influencing the visual sense, DiPT primarily impacts the auditory perception.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 14780-24-6 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 26903 |
| ChemSpider | 25060 |
| UNII | E352B01VMH |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:48286 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID80163804 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H24N2 |
| Molar mass | 244.382 g·mol−1 |
Hallucinogenic properties
The effects of DiPT are predominantly centered on auditory perception. At lower doses, Alexander Shulgin noted effects akin to flanging or phase shifting. However, at medium to higher dosages, DiPT’s impact typically leads to a pronounced downward shift in the perceived pitch. This pitch shift is often nonlinear, meaning that the extent of the downward shift varies relative to the initial pitch, resulting in unusual and disharmonious sounds, particularly when listening to music.
An experiment involving individuals with perfect pitch sought to ascertain whether the pitch difference is genuinely distortive or linear. The results of this study indicated that there needs to be a clear and consistent relationship between the perceived pitch and the actual pitch.
Apart from these auditory effects, another notable non-auditory effect of DiPT is the sensation of inner ear pressure. In some cases, this sensation has been reported as painful, especially when DiPT is combined with substances such as MDMA.
Chemistry
DiPT is a tryptamine derivative created through the replacement of two hydrogen atoms on the non-aromatic nitrogen atom in the tryptamine molecule with isopropyl groups.
Pharmacodynamics
| Binding sites | Binding affinity (Ki, μM) |
|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | 0.538 |
| 5-HT2A | 1.2 |
| 5-HT2C | 6.5 |
| D1 | >25 |
| D2 | >25 |
| D3 | >25 |
| α1A | >12 |
| α2A | 3.6 |
| TAAR1 | >15 |
| H1 | 0.92 |
| SERT | 0.18 |
| DAT | 4.1 |
| NET | 8.9 |
Legal status
United Kingdom
Similar to many compounds featured in PiHKAL and TiHKAL, DiPT is categorized as a Class A substance in the United Kingdom. This classification renders it illegal to possess or use within the country.
United States
At the federal level in the United States, DiPT is not officially scheduled. However, it may be considered an analog of 5-MeO-DiPT, potentially subject to prosecution under the Federal Analog Act if acquired, sold, or possessed for human consumption or illicit purposes rather than for scientific or industrial applications. Notably, during Operation Web Tryp, some individuals faced legal consequences for selling DiPT, even though the drug is not explicitly prohibited.
It’s worth mentioning that the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) retracted a proposal to categorize five psychedelic substances, including 4-Hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (4-OH-DiPT), N-Isopropyl-5-Methoxy-N-Methyltryptamine (5-MeO-MiPT), and N,N-Diisopropyltryptamine (DiPT), as Schedule I controlled substances. This decision followed a public hearing in 2022.
Florida
In the state of Florida, “DiPT (N,N-Diisopropyltryptamine)” holds a Schedule I classification, rendering it illegal to purchase, sell, or possess within the state.
Sweden
Sweden’s public health agency proposed the classification of DiPT as a hazardous substance on May 15, 2019.
FAQ
- What is Diisopropyltryptamine (DiPT)?
- Diisopropyltryptamine, commonly known as DiPT, is a psychedelic compound belonging to the tryptamine class. It is known for its unique auditory effects and is structurally related to other tryptamines.
- What sets DiPT apart from other psychedelics?
- DiPT is distinctive due to its primarily auditory effects. While many psychedelics primarily affect visual perception, DiPT’s hallmark is its impact on the auditory senses.
- Is DiPT legal in the United Kingdom?
- No, DiPT is classified as a Class A substance in the United Kingdom, making it illegal to possess or use within the country.
- How is DiPT regulated in the United States?
- At the federal level in the United States, DiPT is not officially scheduled. However, it could potentially be considered an analog of 5-MeO-DiPT, which may result in legal consequences if acquired, sold, or possessed for human consumption or illicit purposes, rather than for scientific or industrial applications. It’s important to note that its legal status can be complex and subject to change.
- What was the outcome of the DEA’s proposal to ban DiPT and other psychedelic substances?
- The U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) withdrew a proposal to classify DiPT and several other psychedelic substances as Schedule I controlled substances after a public hearing in 2022. As a result, DiPT remains unscheduled at the federal level.
- Is DiPT legal in Florida?
- No, in the state of Florida, DiPT is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance, making it illegal to purchase, sell, or possess.
- What regulatory actions have been taken in Sweden regarding DiPT?
- Sweden’s public health agency proposed classifying DiPT as a hazardous substance on May 15, 2019, reflecting concerns about its potential risks.
- What are the effects of DiPT, particularly its auditory effects?
- DiPT is known for inducing auditory effects, which can include a perceived shift in pitch. At lower doses, effects may be similar to flanging or phase shifting, while at medium and higher dosages, the pitch shift tends to be pronounced and nonlinear, leading to unusual and sometimes disharmonious auditory experiences.
- Are there any medical or therapeutic uses for DiPT?
- DiPT is primarily used for its psychoactive properties and is not approved for medical or therapeutic applications. Research on its potential therapeutic uses is limited.
- What precautions should be taken when dealing with DiPT?
- Due to its unique effects and legal status variations, it is important to be aware of the legal status of DiPT in your region. Individuals should exercise caution when handling or using substances with uncertain legal status, and it is advisable to stay informed about any regulatory changes.
References
- Shulgin A (1997). TiHKAL: Tryptamines I Have Known and Loved. Berkeley, CA USA: Transform Press. This book provides valuable insights into the world of tryptamines, including Diisopropyltryptamine (DiPT). It offers a detailed account of the compound and its effects.
- Rickli A, Moning OD, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (August 2016). “Receptor interaction profiles of novel psychoactive tryptamines compared with classic hallucinogens” (PDF). European Neuropsychopharmacology. This scientific paper explores the receptor interaction profiles of various tryptamines, shedding light on their mechanisms of action and effects.
- “21 CFR — SCHEDULES OF CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES §1308.11 Schedule I.” Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). U.S. Department Of Justice. This official document outlines the scheduling of controlled substances, including the regulatory status of DiPT in the United States.
- “Placement of 4-hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (4-OH-DiPT), 5-methoxy-alpha-methyltryptamine (5-MeO-AMT), 5-methoxy-N-methyl-N-isopropyltryptamine (5-MeO-MiPT), 5-methoxy-N,N-diethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DET), and N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (DiPT) in Schedule I; Withdrawal of Proposed Rule.” This announcement pertains to the proposed scheduling of various substances, including DiPT, as Schedule I controlled substances and their subsequent withdrawal.
- “Chapter 893 – Drug Abuse Prevention and Control.” Florida Statutes. This section of Florida law addresses drug abuse prevention and control, including the scheduling of substances like Diisopropyltryptamine.
- “Folkhälsomyndigheten föreslår att 20 ämnen klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara” (in Swedish). Folkhälsomyndigheten. 15 May 2019. This Swedish report discusses the proposal to classify 20 substances, including DiPT, as narcotics or hazardous goods, reflecting regulatory developments in Sweden.