Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
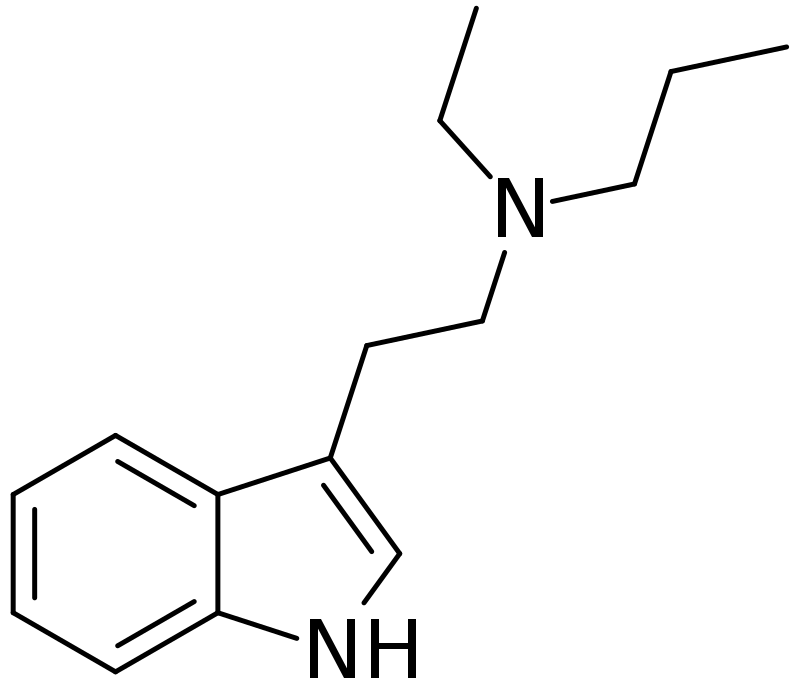
Ethylpropyltryptamine (EPT), also known as N-ethyl-N-propyltryptamine, is an infrequently encountered psychedelic compound belonging to the tryptamine class. This classification establishes its structural similarity to other tryptamines, including DMT, MET, DET, and DPT.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | 850032-68-7 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChemCID | 74405184 |
| UNII | FRE36KL4BD |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C15H22N2 |
| Molar mass | 230.355 g·mol−1 |
Legal status
United Kingdom: The sale, distribution, supply, transport, or trade of this pharmaceutical drug is prohibited under the Psychoactive Substances Act of 2016.
United States: EPT is not scheduled, but it may be deemed an analogue of DMT, a Schedule I substance under the Controlled Substances Act. Consequently, selling it for human consumption could be subject to legality concerns under the Federal Analogue Act.
FAQ
1. What is Ethylpropyltryptamine (EPT)?
- EPT is a chemical compound belonging to the tryptamine class, known for its psychoactive properties and psychedelic effects.
2. Is EPT legal in the United States?
- The legal status of EPT can vary by jurisdiction, but it is generally not controlled at the federal level. However, its legal status may change, and the sale and possession of EPT may be subject to regulation at the state or local level.
3. How does EPT compare to other tryptamines like DMT and psilocybin?
- EPT has a distinct chemical structure and psychoactive profile compared to other tryptamines. It may produce unique subjective experiences and effects differing from those of more well-known psychedelics.
**4. What are the effects of EPT?
- EPT is known for its psychedelic effects, including altered perception, hallucinations, and changes in consciousness. The specific effects and intensity can vary from person to person.
5. Is EPT safe to use?
- The safety of EPT has not been extensively studied, and its long-term effects need to be better understood. As with any psychoactive substance, responsible and cautious use is essential. It is advisable to exercise care, especially if you have no prior experience with it.
6. What are the potential risks associated with EPT use?
- Using EPT, like other psychedelics, carries potential risks such as psychological distress, anxiety, and hallucinogen-persisting perception disorder (HPPD). Additionally, there may be a risk of impurities or contamination when obtaining the substance from unregulated sources.
7. How is EPT typically consumed?
- EPT is commonly taken orally, either in its pure form or as a powder. Other administration methods, such as insufflation (snorting), are less common.
8. Can EPT be used for therapeutic purposes?
- There is limited research on the therapeutic potential of EPT, and it is not approved for any medical or therapeutic use. Other psychedelics like psilocybin and MDMA are more extensively studied for therapeutic applications.
9. Is EPT addictive?
- The addictive potential of EPT is not well understood, but it is generally considered to have a lower risk of physical dependence compared to substances like opioids or stimulants. However, psychological dependence can still occur.
10. Where can I find more information about EPT?
- Given the evolving legal and scientific landscape surrounding EPT, it is important to consult reliable sources of scientific literature and seek advice from healthcare professionals. Staying informed and making well-informed decisions is crucial when considering the use of this substance.
References
- Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Legislation.gov.uk) |http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1971/38/schedule/2/part/I#reference-M_F_c7632653-ddad-4420-f307-e3da1e36d30e