Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
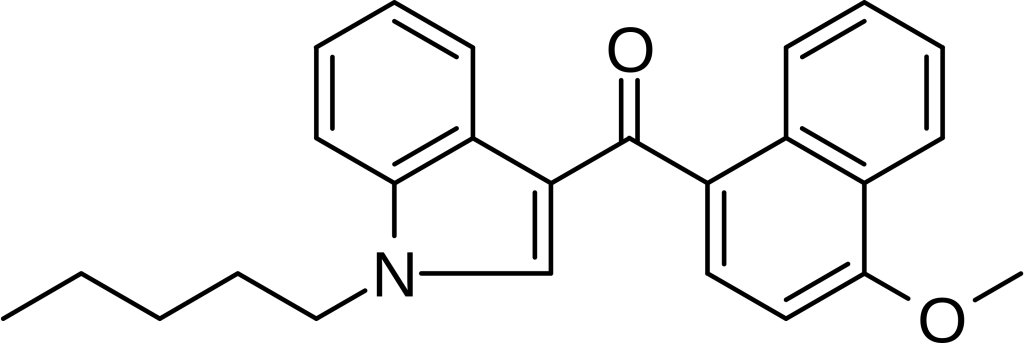
JWH-081, a member of the naphthoylindole family, is an analgesic compound that functions as a cannabinoid agonist, affecting both CB1 and CB2 receptors. It exhibits a degree of selectivity for the CB1 subtype, with a Ki of 1.2nM, making its affinity for CB1 approximately 10 times greater than its affinity for CB2 (12.4nM). This compound was initially identified and named after John W. Huffman.
It’s worth noting that when administered in high doses, JWH-081 may exhibit neurotoxic effects in animals.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 210179-46-7 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 10547208 |
| ChemSpider | 8722599 |
| UNII | 77E58024IT |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID80175225 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.181 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 371.480 g·mol−1 |
Legal status
JWH-081 is classified as a Schedule I Controlled Substance in the United States, and as of October 2015, it is also regulated as a controlled substance in China.
FAQ
- What is JWH-081?
- JWH-081 is a chemical compound from the naphthoylindole family, acting as a cannabinoid agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. It was discovered and named after John W. Huffman, one of its inventors.
- How does JWH-081 work?
- JWH-081 mimics the action of naturally produced endocannabinoid hormones in the body. It primarily binds to the CB1 receptor, although it also has some affinity for the CB2 receptor. The CB1 receptor is mainly found in the brain, while the CB2 receptor is primarily in the immune system.
- Is JWH-081 safe for consumption?
- The safety of JWH-081 is a subject of concern, particularly at high doses. It is neurotoxic in animals when administered in elevated amounts. Using substances like JWH-081 can pose health risks and is often associated with adverse effects.
- What is the legal status of JWH-081 in the United States?
- In the United States, JWH-081 is classified as a Schedule I Controlled Substance. This categorization means it is illegal to manufacture, possess, or distribute this compound due to its potential for abuse and safety concerns.
- Is JWH-081 regulated in other countries?
- Yes, as of October 2015, JWH-081 is also regulated as a controlled substance in China. Different countries may have varying regulations regarding its use and possession.
- Is JWH-081 used for any medical purposes?
- No, JWH-081 is not approved for medical use and should not be used as a medication or for therapeutic purposes. Its potential health risks and safety concerns have limited its acceptance in the medical field.
- What precautions should individuals take regarding JWH-081?
- It is essential to be aware of the legal regulations regarding JWH-081 in your country and avoid any use of this substance for recreational or experimental purposes, given the associated risks. It is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals if you have concerns about its usage.
- Are there any similar compounds to JWH-081?
- Yes, there are other compounds in the same family, such as JWH-018 and JWH-073, synthetic cannabinoids. These compounds may have similar effects and legal statuses in some regions.
- Is there ongoing research about JWH-081?
- Research related to JWH-081 and other synthetic cannabinoids continues to explore their potential effects, both positive and negative. However, these substances remain controversial due to concerns about their safety and legal status.
- Where can I find more information about JWH-081 and related compounds?
- If you are interested in learning more about JWH-081 and related substances, consult reputable sources, such as scientific journals, government drug enforcement agencies, and healthcare professionals, to stay informed about their legal status and potential health risks.
References
- Anvisa, the Brazilian regulatory agency, issued “RDC Nº 804,” listing substances under special control, which includes narcotic, psychotropic, and precursor substances. This resolution guides the legal status of such substances in Brazil.
- The Polish regulation, “Ustawa z dnia 15 kwietnia 2011,” concerning combating drug addiction, outlines amendments related to controlled substances in Poland. It provides legal guidelines and restrictions regarding these substances.
- A study from August 2000 investigates the impact of the N-1 alkyl chain length on the binding of cannabimimetic indoles to CB1 and CB2 receptors. This research contributes to our understanding of the interactions between these compounds and the receptors.
- In January 2005, a study explores the structure-activity relationships of 1-alkyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indoles at the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. The research delves into the steric and electronic effects of naphthoyl substituents on these receptors.
- Recent research in November 2015 highlights the neurotoxicity of synthetic cannabinoids, specifically JWH-081 and JWH-210. This study sheds light on potential health risks associated with these compounds.
- The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) maintains a list of controlled substances, regulating the legal status and restrictions on various substances within the United States.
- China’s “关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知” (Notice on the Control of Non-Medical Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances) issued by the China Food and Drug Administration on September 27, 2015, provides regulatory insights into substances under control in China.