Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
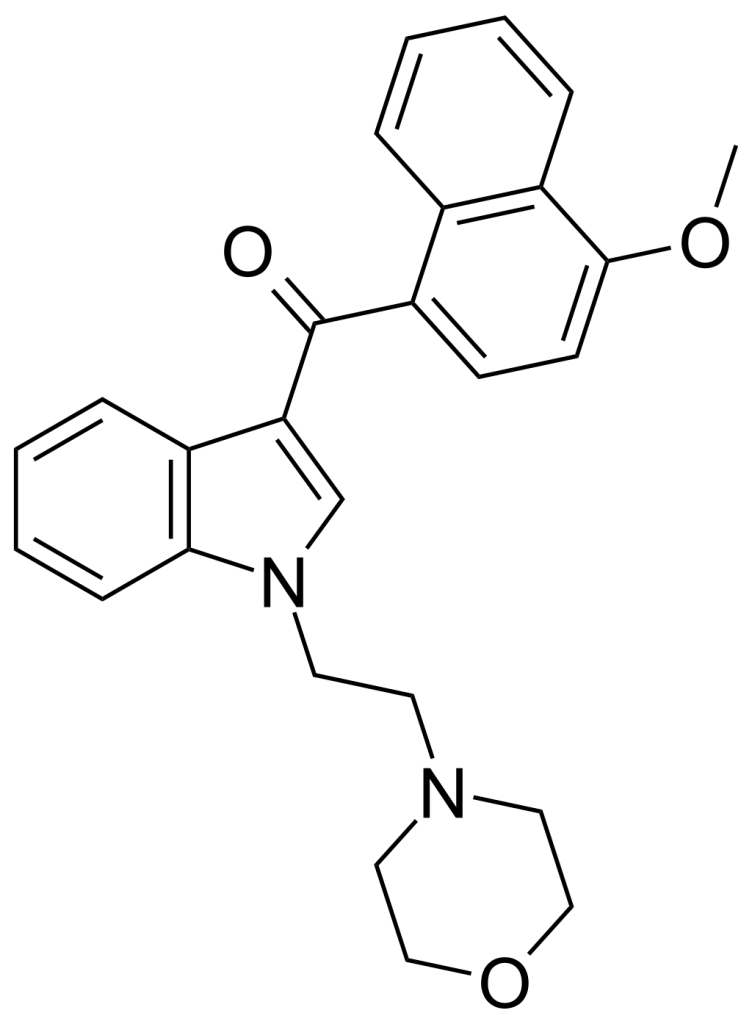
JWH-198 is a medication hailing from both the aminoalkyl indole and naphthoylindole drug families, and it functions as a cannabinoid receptor agonist. This compound was initially developed by the pharmaceutical company Sanofi-Winthrop during the early 1990s. JWH-198 exhibits a notable binding affinity for the CB1 receptor, measuring at 10 nM, approximately four times stronger than its parent compound, JWH-200, which lacks any substitution on the naphthoyl ring. Primarily, JWH-198 has found its application in molecular modeling studies of cannabinoid receptors
It’s important to note that, in the United States, all CB1 receptor agonists belonging to the 3-(1-naphthyl)indole category, such as JWH-198, are classified as Schedule I Controlled Substances. This designation signifies their status as illegal substances under federal law.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 166599-76-4 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 10319620 |
| ChemSpider | 8495084 |
| UNII | J53IGM38PB |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID40168133 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 414.505 g·mol−1 |
FAQ
1. What is JWH-198?
JWH-198 is a medication belonging to the aminoalkylindole and naphthoylindole drug families. It acts as a cannabinoid receptor agonist and was initially developed by Sanofi-Winthrop in the early 1990s.
2. How does JWH-198 function as a cannabinoid receptor agonist?
JWH-198 operates by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the body. It exhibits a significant binding affinity for the CB1 receptor, making it a valuable compound for research and modeling studies related to these receptors.
3. What is the binding affinity of JWH-198 at the CB1 receptor?
JWH-198 demonstrates a binding affinity of 10 nM at the CB1 receptor. This affinity is approximately four times stronger than its parent compound, JWH-200, which lacks any substitution on the naphthoyl ring.
4. What are the applications of JWH-198 in research?
JWH-198 has been primarily used in molecular modeling studies of cannabinoid receptors. Researchers employ this compound to gain insights into the functioning and interactions of cannabinoid receptors, contributing to our understanding of their mechanisms.
5. Is JWH-198 legal in the United States?
No, in the United States, all compounds that act as CB1 receptor agonists and fall within the 3-(1-naphthyl)indole class, including JWH-198, are categorized as Schedule I Controlled Substances. This classification deems them illegal under federal law.
6. What are the potential effects of JWH-198?
JWH-198, as a synthetic cannabinoid, may produce effects similar to natural cannabinoids, including changes in mood and perception. However, its primary use is in research, and it may pose unpredictable and harmful side effects if used recreationally.
7. Is JWH-198 used for medical purposes?
JWH-198 has not been approved for medical use. Its safety and efficacy for medical applications have yet to be established through rigorous testing. For medical conditions, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals and use approved medications.
8. Where can I find more information about JWH-198?
To learn more about JWH-198, consider consulting reputable scientific literature and researchers in the field. Always prioritize safety and adhere to local laws and regulations regarding controlled substances.
References
- Advancements in Cannabimimetic Medicinal Chemistry (2005): Huffman JW and Padgett LW explored recent developments in the medicinal chemistry of cannabimimetic indoles, pyrroles, and indenes in a publication from 2005. This study shed light on the evolving landscape of compounds designed to mimic the effects of cannabinoids. These compounds are significant in research and potentially therapeutic applications.
- Aminoalkylindoles and Cannabinoid Mimetics (August 1995): Eissenstat MA, Bell MR, D’Ambra TE, Alexander EJ, Daum SJ, Ackerman JH, Gruett MD, Kumar V, Estep KG, and Olefirowicz EM conducted research in August 1995, focusing on aminoalkylindoles and their structure-activity relationships as novel cannabinoid mimetics. This study contributed to our understanding of compounds designed to interact with the endocannabinoid system.
- Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) Analysis (November 1998): In November 1998, Shim JY, Collantes ER, Welsh WJ, Subramaniam B, Howlett AC, Eissenstat MA, and Ward SJ performed a three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) study on cannabimimetic (aminoalkyl)indoles using comparative molecular field analysis. This research aimed to elucidate the relationships between the chemical structure of these compounds and their biological activity.
- United States Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. § 812): The United States Controlled Substances Act, as outlined in Section 21 U.S.C. § 812, plays a crucial role in categorizing and regulating controlled substances in the United States. This legislation ensures legal control and safety for various substances, particularly those with the potential for psychoactive effects and misuse.