Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
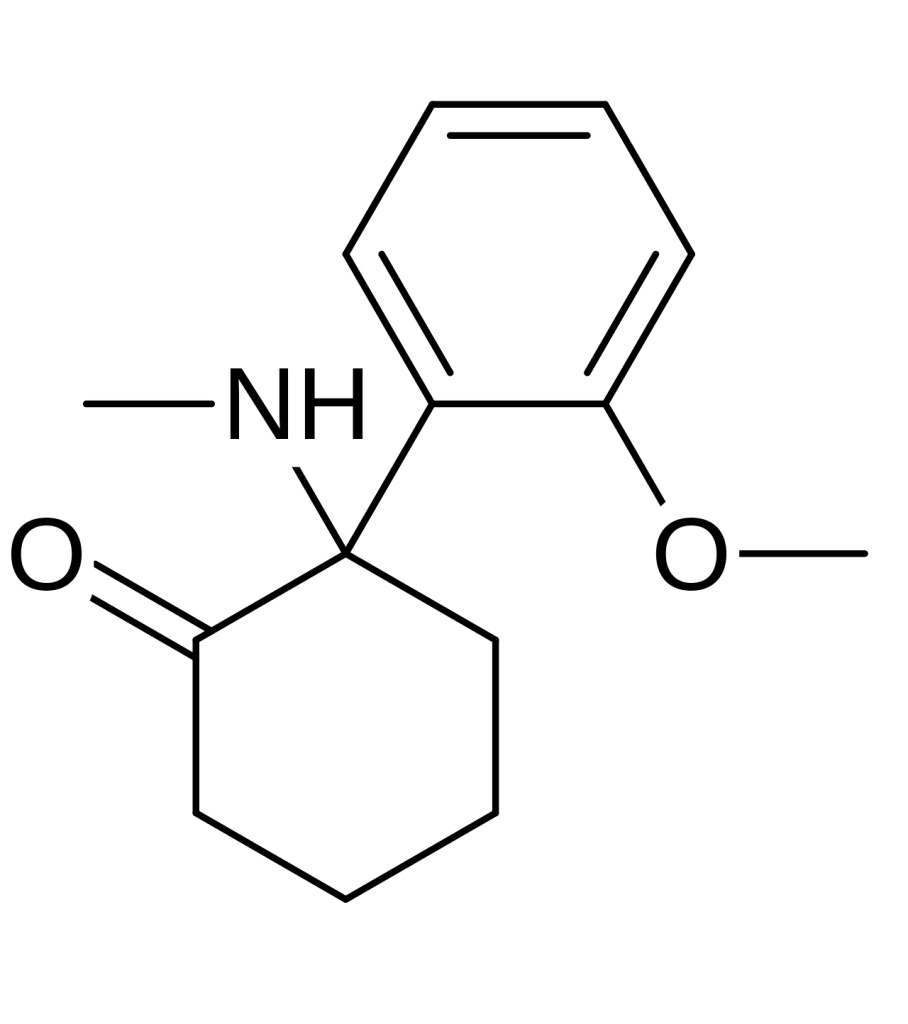
Methoxyketamine, also known as 2-MeO-2-deschloroketamine, is a designer drug belonging to the arylcyclohexylamine class. It was initially documented in 1963. This compound serves as an analog to ketamine, with the chlorine atom replaced by a methoxy group. Its synthesis, involving the rearrangement of an amino ketone, has been detailed in reports.
Being classified as an arylcyclohexylamine, Methoxyketamine is presumed to operate as an NMDA receptor antagonist. It is recognized for inducing sedative, hallucinogenic, and, at higher doses, anesthetic effects, although its potency in these effects is generally lower than that of ketamine itself.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7063-51-6 6728-62-7 (HCl) |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 27470964 |
| PubChemCID | 57483650 |
| UNII | U4I8JIS24N 2OVB5UO35R (HCl) |
| CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | DTXSID30990849 |
FAQ
1. What is Methoxyketamine (2-MeO-2-deschloroketamine)?
Methoxyketamine also referred to as 2-MeO-2-deschloroketamine, is a designer drug belonging to the arylcyclohexylamine class. It is an analog of ketamine, with the chlorine atom replaced by a methoxy group.
2. When was Methoxyketamine first reported?
Methoxyketamine was initially documented in 1963.
3. How is Methoxyketamine synthesized?
Its synthesis involves the rearrangement of an amino ketone and has been reported in scientific literature.
4. What is the presumed mode of action of Methoxyketamine?
Methoxyketamine is considered to function as an NMDA receptor antagonist, similar to ketamine and related compounds.
5. What effects does Methoxyketamine produce?
Methoxyketamine is known to induce a range of effects, including sedation, hallucinations, and, at higher doses, anesthetic effects. However, its potency in these effects is typically lower than that of ketamine itself.
6. Is Methoxyketamine safe for use?
The safety of Methoxyketamine is not well-documented, and its recreational use is associated with potential health risks and adverse effects. Using Methoxyketamine carries inherent risks, and its use is not regulated in many regions.
7. Is Methoxyketamine addictive?
The addictive potential of Methoxyketamine is not extensively studied, but it shares similarities with substances known to have the potential for psychological dependence.
8. Is Methoxyketamine legal?
The legal status of Methoxyketamine varies from one jurisdiction to another. In some areas, it may be considered a controlled or illegal substance, while in others, it may remain unregulated or reserved for research purposes.
9. How can one ensure their safety when dealing with Methoxyketamine?
To prioritize safety, it is essential to stay informed about local regulations, potential health risks, and the legal status of Methoxyketamine in your region. Additionally, always exercise caution and moderation when considering the use of substances like methoxyketamine.
10. Where can I find reliable information about Methoxyketamine?
For accurate and up-to-date information on Methoxyketamine, consult reputable sources such as government health agencies, substance abuse prevention organizations, and medical professionals. It’s crucial to make well-informed decisions when it comes to substances like Methoxyketamine, considering the associated risks and legal implications.
References
- BE 634208, an important patent attributed to Calvin L. Stevens, discusses the realm of “Amino ketones” and was made publicly available in 1963.
- In 1966, a comprehensive study titled “Amino Ketone Rearrangements. VII.1 Synthesis of 2-Methylamino-2-Substituted Phenylcyclohexanones” was conducted by a team of researchers, including Calvin L. Stevens, Andre Thuillier, K. Grant Taylor, Francis A. Daniher, James P. Dickerson, Harry T. Hanson, Norman A. Nielsen, N. A. Tikotkar, and Richard M. Weier. This study, published in The Journal of Organic Chemistry (Volume 31, Issue 8), is accessible with the identifier doi:10.1021/jo01346a034.