Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
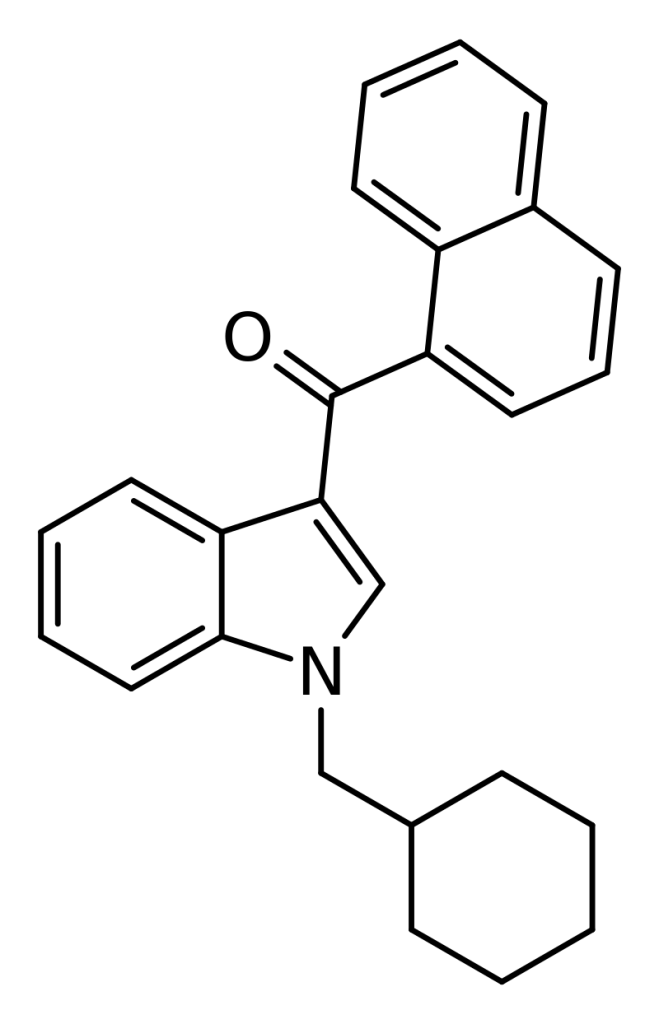
NE-CHMIMO (also known as CHM-018) is a synthetic cannabinoid with an indole base believed to act as a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor. It has gained prominence as a designer drug available for purchase online. NE-CHMIMO distinguishes itself by having a 1-cyclohexyl methyl group instead of the 1-pentyl group found in the first-generation synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018. Notably, a similar cyclohexylmethyl derivative of JWH-081 had been documented a few months before the discovery of NE-CHMIMO.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 1373876-11-9 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 139031057 |
| ChemSpider | 81407778 |
| UNII | 5FWB35TKQ2 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H25NO |
| Molar mass | 367.492 g·mol−1 |
Legal status
In the United States, substances like NE-CHMIMO, which act as CB1 receptor agonists within the 3-(1-naphthyl)indole class, are categorized as Schedule I Controlled Substances. Furthermore, as of November 2019, NE-CHMIMO is designated a controlled substance in Japan.
FAQ
- What is NE-CHMIMO (CHM-018)?
- NE-CHMIMO, also known as CHM-018, is a synthetic cannabinoid. It is considered to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and is often sold online as a designer drug.
- How does NE-CHMIMO differ from other synthetic cannabinoids?
- NE-CHMIMO is the 1-cyclohexylmethyl analog of the first-generation synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018. It has a 1-cyclohexyl methyl group instead of the more common 1-pentyl group found in other synthetic cannabinoids.
- Is NE-CHMIMO legal?
- The legal status of NE-CHMIMO can vary by country and region. In the United States, it is classified as a Schedule I Controlled Substance. In Japan, it is also designated as a controlled substance.
- What are the effects of NE-CHMIMO?
- NE-CHMIMO is presumed to have effects similar to other synthetic cannabinoids, including potential psychoactive and mood-altering effects. However, the specific results can vary from person to person.
- Is NE-CHMIMO safe to use?
- The safety of NE-CHMIMO is a subject of concern. Synthetic cannabinoids can have unpredictable and potentially harmful effects, and their use is associated with health risks. It is essential to exercise caution and be aware of the legal implications in your area.
- Where can I find more information about NE-CHMIMO?
- For the latest information on NE-CHMIMO, legal status, and potential health risks, consult local drug enforcement agencies, health authorities, and official government sources.
References
- Angerer, V., Bisel, P., Moosmann, B., Westphal, F., & Auwärter, V. (September 2016). “Isolation and structural elucidation of the novel synthetic cannabinoid NE-CHMIMO derived from JWH-018 cyclohexyl methyl derivative using flash chromatography, GC-MS, IR, and NMR spectroscopy.” Published in Forensic Science International, 266, pages e93–e98. DOI: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.05.031. PMID: 27297324.
- Franz, F., Jechle, H., Angerer, V., Pegoro, M., Auwärter, V., & Neukamm, M.A. (May 2018). “A Practical Approach to Updating Analytical Methods, Identifying Synthetic Cannabinoids in Hair, and Determining Compound Prevalence and Concentration Ranges in Authentic Hair Samples.” Published in Analytica Chimica Acta, 1006, pages 61–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.12.029. PMID: 30016265.
- “NE-CHMIMO.” In New Synthetic Drugs Database.
- Blakey, K., Boyd, S., Atkinson, S., Wolf, J., Slottje, P.M., Goodchild, K., & McGowan, J. (March 2016). “Discovery of the novel synthetic cannabimimetic compound QMPSB (8-quinolinyl 4-methyl-3-(1-piperidinylsulfonyl)benzoate) and other designer drugs in herbal incense.” Published in Forensic Science International, 260, pages 40–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.12.001. PMID: 26795397.
- “21 U.S.C. § 812: Schedules of controlled substances.”
- “指定薬物を指定する省令が公布されました|厚生労働省.” (in Japanese) Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Retrieved 2019-12-22.