- 1 Summary
- 2 Chemistry
- 3 Effects
- 4 Legal status
- 5 FAQ
- 5.1 1. What is Buphedrone?
- 5.2 2. Is Buphedrone legal?
- 5.3 3. How is Buphedrone typically consumed?
- 5.4 4. What are the effects of Buphedrone?
- 5.5 5. What are the risks associated with Buphedrone use?
- 5.6 6. Is Buphedrone safe to use?
- 5.7 7. How can I get help for Buphedrone addiction or its effects?
- 5.8 8. Can Buphedrone be used for any medical purposes?
- 5.9 9. Are there any known interactions with other substances or medications?
- 6 References
Summary
Buphedrone, scientifically referred to as α-methylamino-butyrophenone (MABP), belongs to the phenethylamine and cathinone chemical classes. It was initially synthesized in 1928. It’s essential to note that buphedrone is generally considered legal in many countries when classified as a research chemical, provided it is not intended for human consumption.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 408332-79-6 166593-10-8 (hydrochloride) |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 53249194 |
| ChemSpider | 26286946 |
| UNII | VD73947M0O |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID701014170 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO |
| Molar mass | 177.247 g·mol−1 |
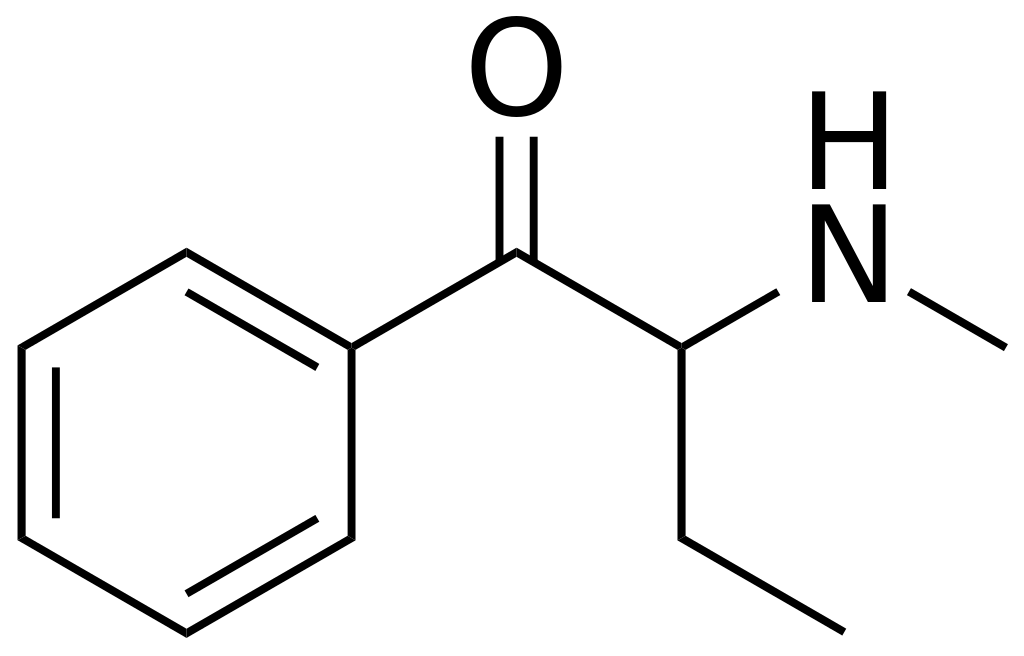
Chemistry
Buphedrone is classified as a beta-ketone compound and shares chemical connections with naturally occurring substances such as cathinone and cathine. Additionally, it exhibits a structural similarity to methamphetamine, albeit with distinct features, including the presence of a β-ketone substituent at the beta carbon and an ethyl group replacing the methyl group adjacent to the amine. Another designation for buphedrone is phenylacetoethyl-methylamine.
In its free base form, buphedrone is exceptionally unstable and prone to dimerization, a common characteristic among α-amino ketones. Due to this instability, buphedrone is typically marketed in various salt forms, with the hydrochloride variant being the most prevalent.
Effects
Buphedrone exerts several effects on spontaneous rodent locomotor activity, including an increase in such activity. It also enhances the release of dopamine from dopaminergic nerve terminals in the brain and leads to appetite suppression. Additionally, it can induce a potentially risky phenomenon by reducing the subjective sensation of thirst. Comparatively, buphedrone’s effects have been likened to those of methamphetamine, characterized by heightened euphoria and reduced physical stimulation. The most frequently reported effects encompass:
- Elevated mood and euphoria
- Enhanced alertness
- Occasional pupil dilation
- Rare instances of slurred speech
- Elevated heart rate
- Increased talkativeness
- Enhanced empathy and improved communication
- Elevated sex drive
- Temporary erectile dysfunction in men
- Restlessness
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Increased motivation
The duration of these effects varies depending on the administration route, spanning approximately 2.5 hours (intravenous) to 6 hours (oral). Following this, users may experience unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, including:
- Dysphoria
- Fatigue
- Sweating
- Difficulty maintaining concentration
Legal status
By October 2015, buphedrone had been categorized as a controlled substance in China.
Buphedrone is classified as an Anlage II controlled drug in Germany.
In the United States, ephedrine is designated as a Schedule I controlled substance due to its status as a positional isomer of Mephedrone.
FAQ
1. What is Buphedrone?
Buphedrone is a synthetic psychoactive substance belonging to the family of substituted cathinones. It is chemically related to drugs like methcathinone and mephedrone, and it acts as a stimulant.
2. Is Buphedrone legal?
The legality of Buphedrone varies from country to country and even within different regions of the same country. It’s important to check your local laws and regulations regarding the possession, sale, or use of Buphedrone before considering its use.
3. How is Buphedrone typically consumed?
Buphedrone is most commonly found in a white powder form and is often ingested by snorting, swallowing, or even injecting. However, its use can be dangerous and is associated with several health risks.
4. What are the effects of Buphedrone?
The effects of Buphedrone are similar to those of other stimulant drugs. Users typically experience increased alertness, energy, and a sense of euphoria. However, it can also lead to negative effects such as anxiety, paranoia, and an increased heart rate. Long-term use can have more severe health consequences.
5. What are the risks associated with Buphedrone use?
Buphedrone use can be dangerous and is associated with a range of risks and adverse effects, including:
- Addiction: Buphedrone has a high potential for abuse and addiction.
- Physical health: It can lead to cardiovascular issues, high blood pressure, and damage to internal organs.
- Mental health: Buphedrone use can result in anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations, and mood swings.
- Legal consequences: Possession and distribution of Buphedrone can lead to legal troubles.
6. Is Buphedrone safe to use?
No, Buphedrone is not considered safe for use. It is an unregulated and potentially harmful substance. Its safety and quality can vary significantly between different sources, making it even more dangerous. Users should avoid using Buphedrone and seek help if they have already used it and are experiencing adverse effects.
7. How can I get help for Buphedrone addiction or its effects?
If you or someone you know is struggling with Buphedrone addiction or its effects, it’s essential to seek help immediately. You can contact local addiction support organizations, medical professionals, or mental health services for assistance. Substance abuse treatment and counselling are effective ways to address addiction and its associated problems.
8. Can Buphedrone be used for any medical purposes?
No, Buphedrone is not approved for any medical purposes and is not prescribed by healthcare professionals. It is a recreational drug with no recognized medical benefits.
9. Are there any known interactions with other substances or medications?
Buphedrone can interact with other substances, including prescription medications. These interactions can be dangerous and may lead to adverse effects. It is crucial to disclose any substance use, including Buphedrone, to your healthcare provider if you are prescribed medications.
References
- Hyde JF, Browning E, Adams R’s groundbreaking research in August 1928, published in the “Journal of the American Chemical Society,” sheds light on “Synthetic Homologs of d,l-Ephedrine” (doi:10.1021/ja01395a032), marking a significant milestone in the field of chemistry.
- In a Chinese document titled “关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知,” issued by the China Food and Drug Administration on September 27, 2015, regulatory guidelines for non-medicinal narcotics and psychotropic substances were disseminated, reflecting China’s commitment to drug control (in Chinese).
- The U.S. Department of Justice, in its “Lists of: Scheduling Actions Controlled Substances Regulated Chemicals” (PDF) released in February 2023, provides a comprehensive overview of scheduling actions and regulated chemicals, offering valuable insights into the legal control of substances in the United States (accessed on March 7, 2023).
