Beautiful Plants For Your Interior
Summary
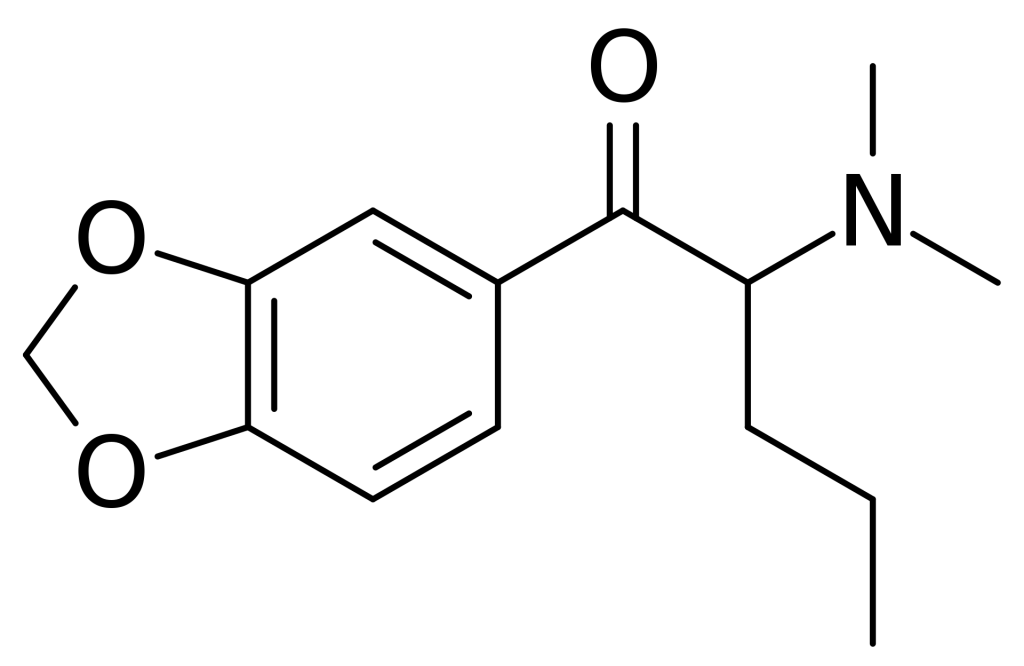
N,N-Dimethylpentylone, commonly referred to as Dipentylone or simply Dimethylpentylone, is a derivative of cathinone with stimulant properties. This compound has been marketed as a designer drug and was initially identified in Sweden in 2014.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 803614-36-0 17763-13-2 (Hydrochloride) |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 119057570 |
| ChemSpider | 52085278 |
| UNII | V41961I345 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H19NO3 |
| Molar mass | 249.310 g·mol−1 |
Metabolism and pharmacology
Pentylone is a known metabolite of Dimethylpentylone.
Society and Culture
Dimethylpentylone was first detected in toxicology samples in the United States towards the end of 2021. The Center for Forensic Science Research and Education (CFSRE) has closely monitored its presence through the NPS Discovery program. It has been observed that Dimethylpentylone is increasingly being mislabeled and sold as MDMA, similar to the trend previously seen with Eutylone being misrepresented as MDMA.
On June 26, 2023, the United States Customs and Border Protection intercepted a shipment of 32.2 kilograms of Dimethylpentylone. This shipment, originating from China and falsely labeled as “beauty products,” was destined for an address in Washington, D.C.
Furthermore, on July 10, 2023, an interview with Jacksonville DEA Assistant Special Agent in Charge Mike Dubet revealed that Dimethylpentylone has been discovered in the possession of individuals frequenting nightclubs and bars in the Jacksonville, Florida area.
Legality
In the United States, Dimethylpentylone is not explicitly designated under the Controlled Substances Act. However, it would be categorized as a Schedule I substance due to its status as a positional isomer of N-Ethylpentylone, which is a Schedule I substance in the United States. The definition of “all isomers” within that context encompasses Dimethylpentylone within this classification.
FAQ
- What is Dipentylone?
- Dipentylone, also known as N, N-Dimethylpentylone, is a synthetic cathinone compound with stimulant effects. It is chemically related to other substances in the cathinone family.
- What are the effects of Dipentylone?
- Dipentylone is known for its stimulant properties, often leading to increased alertness, energy, and a sense of euphoria. However, its effects can vary depending on the individual and the dose used.
- Is Dipentylone legal?
- The legal status of Dipentylone varies from one jurisdiction to another. In some places, it may be controlled as a substance of abuse, while in others, it may not be precisely regulated. It is essential to research and understand the laws in your area.
- How is Dipentylone typically used?
- Dipentylone is most commonly encountered as a designer drug and may be sold in various forms, including powders or capsules. It is typically ingested orally, but other routes of administration are also possible.
- What are the potential risks and side effects of Dipentylone use?
- The use of Dipentylone can be associated with side effects such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, anxiety, insomnia, and potential adverse psychological effects. The long-term health risks of using this substance are not well understood.
- Is Dipentylone similar to MDMA (Ecstasy)?
- While Dipentylone may produce stimulant and empathogenic effects similar to MDMA, it is chemically distinct. Users should be cautious and aware that the purity and contents of substances sold as Dipentylone may vary.
- Can Dipentylone be addictive?
- Like many stimulant substances, Dipentylone has the potential for abuse and addiction, especially with frequent or high-dose use. Addiction risks can increase with compulsive or irresponsible use.
- Where can I find more information about Dipentylone and its legal status?
- Information on Dipentylone and its legal status can be obtained from local drug enforcement agencies or government websites focusing on drug regulations and policies. Staying informed and adhering to local laws is crucial.
- Is Dipentylone safe for use?
- The safety of Dipentylone is not well-established, and it is not approved for any medical or therapeutic use. Using this substance can carry various health risks, and individuals should exercise caution and consider potential consequences.
- Are there harm reduction measures for Dipentylone use?
- Harm reduction strategies, such as using substance testing services, avoiding high doses, and staying hydrated, can help minimize risks associated with Dipentylone use. However, the safest approach is to refrain from using such substances altogether.
References
- Gatch MB, Shetty RA, Sumien N, Forster MJ (July 2021). “Exploring the Behavioral Effects of Four Novel Synthetic Cathinone Analogs in Rodents.” This research delves into the behavioral impacts of four newly developed synthetic cathinone analogs in rodent subjects. [Reference: Addiction Biology, 26(4), e12987]
- Celma A, Sancho JV, Salgueiro-González N, Castiglioni S, Zuccato E, Hernández F, Bijlsma L (September 2019). “Simultaneous Detection of New Psychoactive Substances and Illicit Drugs in Sewage: Micro-Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Wastewater-Based Epidemiology.” This study explores the potential of micro-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous identification of new psychoactive substances and illicit drugs in sewage, contributing to wastewater-based epidemiology. [Reference: Journal of Chromatography A, 1602, 300–309]
- “Police and Drug Agency Issue Warning After Discovery of New Drug in Dunedin.” A strong cautionary alert was issued by law enforcement and drug agencies following the detection of a new drug in Dunedin. [Reference: New Zealand Herald, 8 December 2021]
- “Europol 2014 Annual Report on the Implementation of Council Decision.” This report, prepared by the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) and Europol, provides insights into the implementation of Council Decision 2005/387/JHA in 2014.
- “Synthetic Stimulant Market Undergoes Rapid Changes with N,N-Dimethylpentylone Replacing Eutylone in Drug Supply Commonly Sold as ‘Ecstasy’ or ‘Molly’.” A report highlighting the dynamic shifts in the synthetic stimulant market, where N,N-Dimethylpentylone has begun to replace Eutylone in drug supplies often sold as ‘Ecstasy’ or ‘Molly.’ [Published on 20 April 2022]
- “Dulles CBP Officers Seize 70 Pounds of a Dangerous, Newer Cathinone Analogue Destined for D.C.” U.S. Customs and Border Protection announced the seizure of 70 pounds of a hazardous cathinone analog from China, falsely labeled as beauty products and intended for Washington, D.C. [Source: www.cbp.gov, Retrieved 2023-08-10]
- “70 Pounds of Psychoactive Drugs from China Labeled as Beauty Products Seized at US Airport.” A significant interception of 70 pounds of psychoactive drugs from China, falsely declared as beauty products, occurred at a U.S. airport. [Published on 2023-07-06, Retrieved 2023-08-10]
- Avanier, Erik (2023-07-11). “Newest Street Drug Emerges in Northeast Florida Nightclubs and Bars.” An investigative report sheds light on the emergence of a new street drug, which has found its way into nightclubs and bars in Northeast Florida. [Source: WJXT, Retrieved 2023-08-10]
- “2020 – Placement of N-Ethylpentylone in Schedule I.” This document outlines the placement of N-Ethylpentylone into Schedule I, which includes substances with a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use.
- “2007 – Definition of ‘Positional Isomer’ as It Pertains to the Control of Schedule I Controlled Substances.” This document presents the definition of ‘Positional Isomer’ in the context of regulating Schedule I controlled substances.