Summary
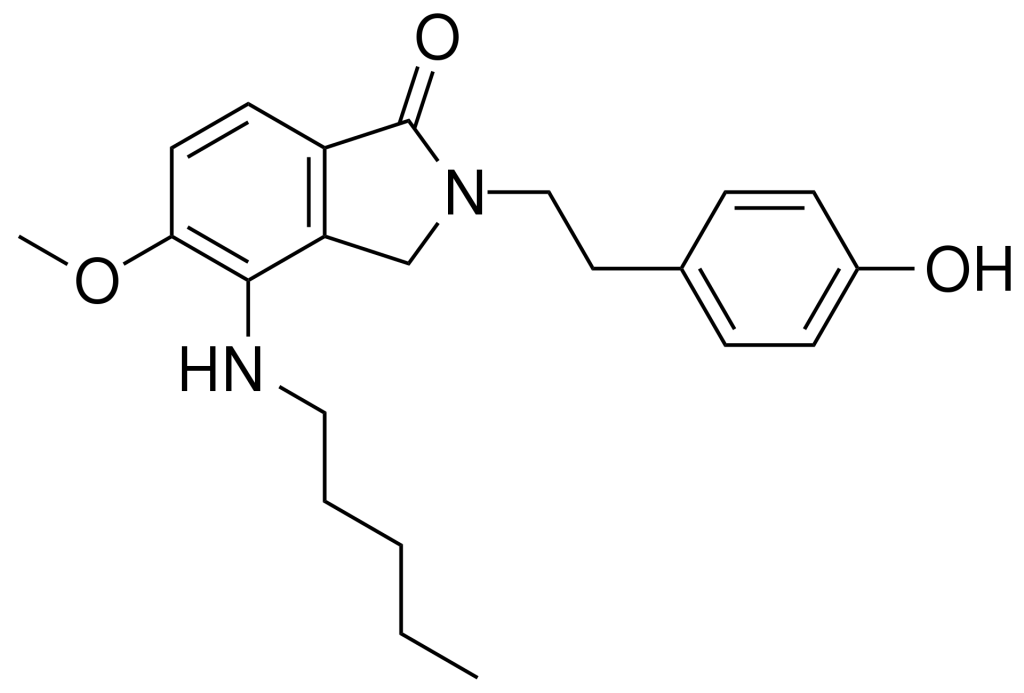
JTE 7-31, a creation of Japan Tobacco, emerges as a selective agonist for cannabinoid receptors. This compound exhibits significant selectivity for CB2 receptors, yet it maintains a noteworthy affinity for CB1 receptors, boasting a Ki of 0.088nM at CB2 compared to 11nM at CB1.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | 194358-72-0 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 13767708 |
| PubChemCID | 19363402 |
| UNII | 7MV5OX2NX0 |
| CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | DTXSID50598386 |
Legality
JTE 7-31 is illegal in Alabama.
FAQ
1. What is JTE 7-31?
- JTE 7-31 is a compound invented by Japan Tobacco. It is a selective cannabinoid receptor agonist designed for research purposes.
2. What Does “Selective Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist” Mean?
- A selective cannabinoid receptor agonist is a compound that primarily activates specific cannabinoid receptors. In the case of JTE 7-31, it demonstrates a preference for CB2 receptors.
3. What Are CB1 and CB2 Receptors?
- CB1 and CB2 receptors are part of the endocannabinoid system in the human body. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are more prevalent in the immune system and peripheral tissues.
4. How Selective is JTE 7-31 for CB2 Receptors?
- JTE 7-31 exhibits high selectivity for CB2 receptors. This means it has a strong affinity for CB2 receptors and has limited activity on CB1 receptors.
5. What is Ki in the Context of Receptor Affinity?
- Ki (inhibition constant) measures the affinity of a ligand (such as JTE 7-31) for a specific receptor. A lower Ki value indicates a higher affinity for the receptor.
6. What Is the Significance of JTE 7-31’s Affinity for CB1 Receptors?
- While JTE 7-31 is highly selective for CB2 receptors, it still has some affinity for CB1 receptors. This affinity could have implications in research or potential applications, as the compound may interact with both receptor types.
7. Is JTE 7-31 Available for Personal Use or Prescription?
- JTE 7-31 is primarily used as a research tool and is not typically available for personal use or prescription. It is designed for scientific investigations and may not be approved for human use.
8. What Are the Potential Research Applications of JTE 7-31?
- JTE 7-31’s selectivity for CB2 receptors makes it a valuable tool for studying the functions of these receptors. Researchers may use it to investigate the role of CB2 receptors in various physiological processes.
9. Is JTE 7-31 Psychoactive?
- JTE 7-31 is not typically associated with psychoactive effects, as it primarily interacts with cannabinoid receptors that are not linked to the typical psychoactive properties of compounds like THC.
10. Where Can I Find More Information About JTE 7-31?
- To learn more about JTE 7-31, you can refer to scientific literature research publications or consult with experts in the field. Remember that it is primarily a research compound, and its availability for general information may be limited.
References
- Explore the historical patents that mark the origin of JTE 7-31: WO patent 1997/029079, credited to Inaba T, Kaya T, and Iwamura H, “Revealing Novel Compounds and Their Pharmaceutical Applications,” granted on August 14, 1997.
- Witness the evolution of JTE 7-31 with the US patent 6017919, also attributed to Inaba T, Kaya T, and Iwamura H, titled “Compounds and Their Pharmaceutical Uses,” granted on January 25, 2000.
- Delve into the world of research and development with a study by Han S, Zhang FF, Qian HY, Chen LL, Pu JB, Xie X, and Chen JZ (March 2015). “Unearthing the Secrets of Coumarin Derivatives: Design, Syntheses, Structure-Activity Relationships, and Docking Studies as Novel Selective Ligands for the CB2 Receptor.” Published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 93, 16–32. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.054. PMID: 25644673.
- Stay informed about legislative matters with “Alabama Senate Bill SB 333: Controlled Substances” (PDF).