Summary
Meprylcaine, also known as Epirocaine and Oracaine, is a local anesthetic featuring stimulant characteristics and shares a structural resemblance with dimethocaine.
This compound boasts a noteworthy capacity to inhibit monoamine transporters, effectively impeding the reuptake of crucial neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 495-70-5 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 4065 |
| ChemSpider | 3925 |
| UNII | 82YT7WU9PW |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL127810 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID70197810 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 235.327 g·mol−1 |
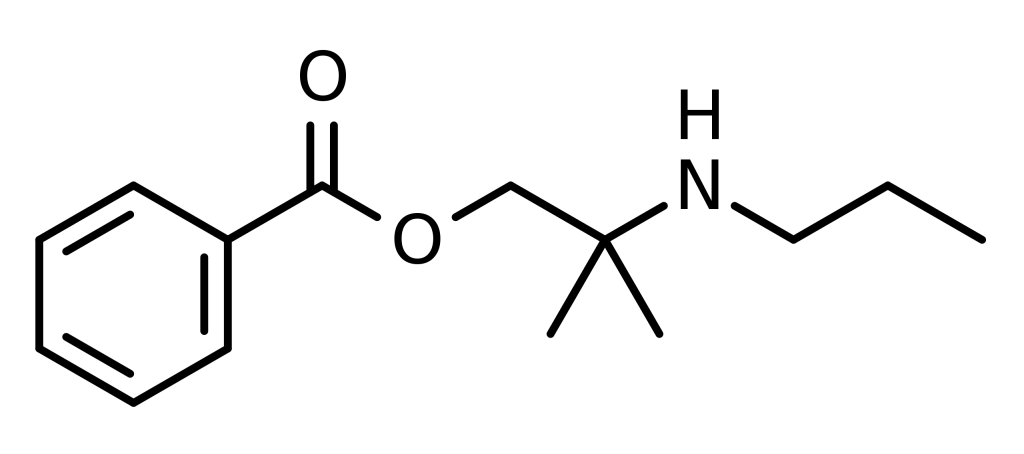
Synthesis
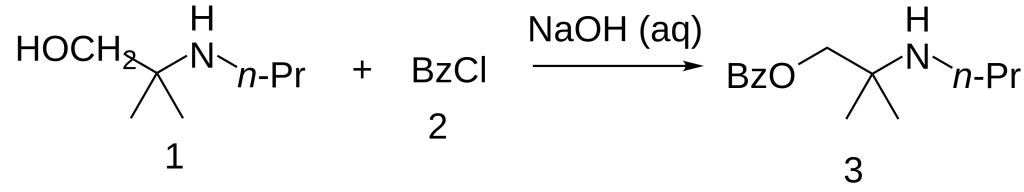
The 2-methyl-2-(propylamino)propan-1-ol [55968-10-0] (1) is treated with base and then with Benzoyl chloride (2), completing the synthesis of Meprycaine (3).
FAQ
- What is Meprylcaine?
- Meprylcaine, known by its alternative names Epirocaine and Oracaine, is a compound categorized as a local anesthetic with stimulant properties. It exhibits structural similarities to dimethocaine, another compound used for its anesthetic effects.
- How does Meprylcaine work?
- Meprylcaine functions by inhibiting the monoamine transporters in the body. This inhibitory action prevents the reuptake of several important neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. These neurotransmitters are vital in mood regulation, alertness, and overall brain function.
- What are the uses of Meprylcaine?
- Meprylcaine is primarily employed as a local anesthetic, used to induce a loss of sensation in a specific body area. The stimulant properties of Meprylcaine make it useful in some medical contexts. However, its usage should be supervised by a healthcare professional.
- Is Meprylcaine legal?
- The legal status of Meprylcaine varies from one region to another. It may be classified as a controlled substance or regulated as a prescription drug in some areas. It is important to be aware of and comply with local laws and regulations regarding Meprylcaine.
- Are there any side effects associated with Meprylcaine?
- Meprylcaine, like many drugs, can have side effects. These side effects may include increased heart rate, restlessness, and potential effects on mood and alertness. It’s essential to use Meprylcaine only as directed by a medical professional to minimize these side effects.
- Can Meprylcaine be misused or abused?
- Yes, Meprylcaine has the potential for misuse and abuse, particularly due to its stimulant properties. In some cases, individuals may misuse this compound for non-medical purposes, seeking its stimulant effects. Misuse of Meprylcaine can have health risks and may be illegal in some regions.
- Is Meprylcaine available over the counter?
- The availability of Meprylcaine over the counter varies depending on the region and local regulations. In some places, it may be available only with a prescription, while in others, it may be regulated more strictly.
- Can Meprylcaine interact with other medications or substances?
- Yes, Meprylcaine has the potential to interact with other medications and substances. If you are taking other drugs or have any underlying health conditions, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using Meprylcaine to prevent potential interactions and health risks.
- Is Meprylcaine safe for everyone?
- Meprylcaine may be unsafe for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions or sensitivities. It is essential to seek guidance from a healthcare provider before using Meprylcaine to determine its safety and appropriateness for your specific situation.
- Where can I get more information about Meprylcaine?
- For more detailed and region-specific information about Meprylcaine, consult a healthcare professional or a pharmacist or refer to local drug regulations and guidelines in your area.
References
- Selective Inhibition of Monoamine Neurotransmitter Transporters by Synthetic Local AnestheticsSato T, Kitayama S, Mitsuhata C, Ikeda T, Morita K, Dohi T (February 2000). “Selective inhibition of monoamine neurotransmitter transporters by synthetic local anesthetics”. This study was published in the journal “Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology” and delved into the selective inhibition of monoamine neurotransmitter transporters by synthetic local anesthetics. [DOI: 10.1007/s002109900184] [PMID: 10685879] [S2CID: 1627097].
- Chronic Inhibition of the Norepinephrine Transporter and Its Role in Seizure SensitizationArai S, Morita K, Kitayama S, Kumagai K, Kumagai M, Kihira K, Dohi T (February 2003). “Chronic inhibition of the norepinephrine transporter in the brain participates in seizure sensitization to cocaine and local anesthetics.” This research, published in “Brain Research,” explored the chronic inhibition of the norepinephrine transporter and its involvement in seizure sensitization to cocaine and local anesthetics. [DOI: 10.1016/S0006-8993(02)04068-4] [PMID: 12573515] [S2CID: 16539422].
- Inhibition of Serotonin Transporters and Seizure Activities Facilitated by Cocaine and MeprylcaineMorita K, Hamamoto M, Arai S, Kitayama S, Irifune M, Kawahara M, et al. (September 2005). “Inhibition of serotonin transporters by cocaine and meprylcaine through 5-TH2C receptor stimulation facilitates their seizure activities” (PDF). This study, featured in “Brain Research,” investigates the inhibition of serotonin transporters by cocaine and meprylcaine, highlighting their role in facilitating seizure activities through 5-TH2C receptor stimulation. [DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.07.049] [PMID: 16125150] [S2CID: 30437231].
- Esters of β-AlkylaminoethanolsReasenberg, Julian R.; Goldberg, Samuel D. (1945). “Esters of β-Alkylaminoethanols”. This publication in the “Journal of the American Chemical Society” from 1945 discusses the esters of β-alkylaminoethanols, providing valuable insights into chemical compounds. [DOI: 10.1021/ja01222a017].
- Julian R Reasenberg’s Patent on Methanesulfonate EstersJulian R Reasenberg, U.S. Patent 2,767,207 (1956 to Mizzy Inc). This patent, granted in 1956, is attributed to Julian R Reasenberg and relates to methanesulfonate esters.
- Patent on Esters of β-AlkylaminoethanolsJulian R Reasenberg, Samuel D Goldberg, U.S. Patent 2,421,129 (1947 to Oradent Chemical Co Inc). This patent, awarded in 1947 to Julian R Reasenberg and Samuel D Goldberg, concerns esters of β-alkylaminoethanols, shedding light on their chemical properties and applications.