Contents
Summary
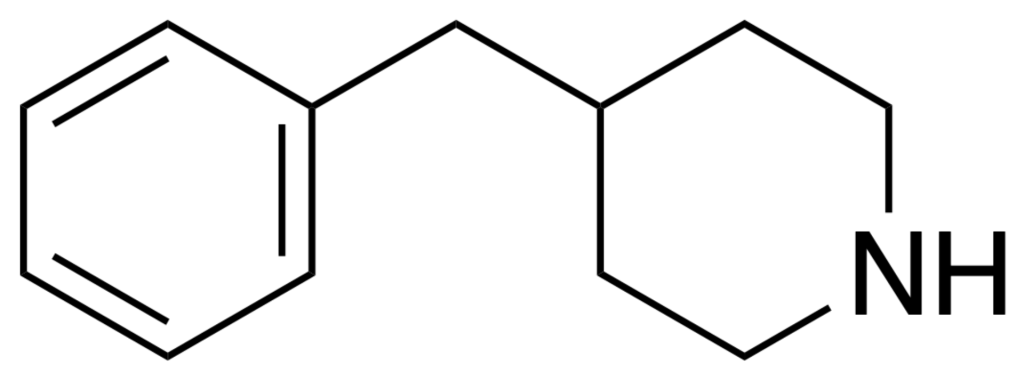
4-Benzylpiperidine is a chemical compound that falls under the class of piperidines, which are heterocyclic compounds containing a six-membered ring structure. It is a synthetic compound with potential pharmaceutical applications, primarily in the development of various drugs and medications. The mixture is characterized by the presence of a piperidine ring, which is a saturated nitrogen-containing ring structure, and a benzyl group attached to it.
Effects
The effects of 4-Benzylpiperidine can vary depending on its specific use and context. It is not commonly used as a recreational drug, but it can have different effects when incorporated into pharmaceuticals. As a piperidine derivative, it may exhibit analgesic (pain-relieving) properties, and it has been studied for its potential use in the development of opioid-based medications. However, like many compounds in this class, it also has the potential for abuse and dependence.
Dosage
The dosage of 4-Benzylpiperidine can vary widely depending on the specific drug or medication in which it is used. It is typically administered in pharmaceutical formulations rather than as a standalone compound. Healthcare professionals determine dosage recommendations that are specific to the intended medical condition and patient’s needs. Self-administration of 4-Benzylpiperidine is strongly discouraged due to its potential for adverse effects and abuse.
Toxicity
The toxicity of 4-Benzylpiperidine is a subject of concern, especially when it is misused or in large quantities. Like other piperidine derivatives, it can have adverse effects on the central nervous system and respiratory function. Overdose or misuse can lead to symptoms such as respiratory depression, dizziness, nausea, and, in severe cases, it can be life-threatening. It is essential to handle this compound with care and only under the guidance of qualified medical professionals.
Legal Status
The legal status of 4-Benzylpiperidine can vary by country and region. In many jurisdictions, it is regulated as a controlled substance due to its potential for misuse and abuse. Its legal status is often tied to its use in pharmaceuticals and whether it is classified as a prescription medication or a controlled substance. Individuals should be aware of and adhere to the laws and regulations governing the use and possession of this compound in their respective areas.
Pharmacology
4-Benzylpiperidine’s pharmacology primarily relates to its interaction with the opioid receptors in the central nervous system. Opioid receptors play a crucial role in pain perception, and drugs that interact with these receptors can have analgesic effects. However, they also carry the risk of tolerance, dependence, and addiction. Therefore, the pharmacological properties of 4-benzylpiperidine make it a subject of interest in the development of pain-relief medications and potential treatments for opioid addiction.
Chemistry
From a chemical perspective, 4-benzylpiperidine is a complex molecule. Its chemical structure consists of a piperidine ring, which is a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom and a benzyl group attached to it. The presence of the benzyl group modifies its properties and may influence its interactions with biological systems. The synthesis of 4-Benzylpiperidine involves several chemical steps and requires expertise in organic chemistry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 4-Benzylpiperidine is a chemical compound with diverse potential applications, primarily in the field of pharmaceuticals. Its effects, dosage, toxicity, legal status, and pharmacology are all subject to various considerations and regulations. While it may have therapeutic uses, its potential for misuse and dependence makes it a compound that should only be handled and administered by qualified healthcare professionals. The legal status of 4-Benzylpiperidine varies by jurisdiction, and individuals should be aware of and adhere to the laws governing its use and possession in their respective regions. Overall, 4-benzylpiperidine exemplifies the complex relationship between chemistry, pharmacology, and regulation in the realm of pharmaceuticals and controlled substances.
FAQ
1. What is 4-Benzylpiperidine?
- 4-Benzylpiperidine is a synthetic chemical compound classified as a piperidine derivative. It has applications in the pharmaceutical industry and is of interest due to its potential as a precursor in the synthesis of various medications.
2. What are the effects of 4-Benzylpiperidine?
- The effects of 4-Benzylpiperidine can vary depending on its specific use. It has been studied for its potential analgesic (pain-relieving) properties and its role in the development of opioid-based medications. However, it also has a potential for misuse and dependence.
3. Is 4-Benzylpiperidine used recreationally?
- It is not commonly used as a recreational drug. Instead, it is primarily utilized in pharmaceutical research and development.
4. What is the recommended dosage of 4-Benzylpiperidine?
- Dosage recommendations for 4-Benzylpiperidine are determined by healthcare professionals when it is used as a component in pharmaceuticals. Self-administration is strongly discouraged due to the compound’s potential for adverse effects.
5. What is the toxicity of 4-Benzylpiperidine?
- 4-Benzylpiperidine can be toxic, especially when misused or taken in excessive amounts. Overdose can result in symptoms such as respiratory depression, dizziness, nausea, and, in severe cases, life-threatening consequences.
6. What is the legal status of 4-Benzylpiperidine?
- The legal status of 4-Benzylpiperidine varies by country and region. In many places, it is regulated as a controlled substance due to its potential for misuse and abuse. It may also be classified based on its use in pharmaceuticals.
7. How does 4-Benzylpiperidine work pharmacologically?
- 4-Benzylpiperidine interacts with opioid receptors in the central nervous system. This interaction can produce analgesic effects, making it of interest in the development of pain-relief medications and potential treatments for opioid addiction.
8. What is the chemical structure of 4-benzylpiperidine?
- 4-Benzylpiperidine consists of a piperidine ring, which is a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom with a benzyl group attached to it. This chemical structure affects its properties and interactions with biological systems.
9. Can individuals purchase 4-Benzylpiperidine for personal use?
- Generally, 4-Benzylpiperidine is not available for personal use. It is primarily used in research and pharmaceutical development, and its distribution is highly regulated due to its potential for misuse.
10. Is 4-Benzylpiperidine related to illicit drugs like opioids? – 4-Benzylpiperidine itself is not an illicit drug, but it is chemically related to opioids due to its interactions with opioid receptors. Its use in pharmaceutical research is focused on potential opioid-related applications.
11. Are there any known medical uses for 4-Benzylpiperidine? – 4-Benzylpiperidine is primarily a research chemical and is not used as a standalone medication. Its potential medical applications are within the realm of developing pharmaceuticals for pain relief and addiction treatment.
12. Can 4-Benzylpiperidine be obtained without a prescription? – Typically, 4-Benzylpiperidine is not available without a prescription, and its distribution is controlled to prevent misuse and unauthorized access.
References
- In a study conducted by Negus SS, Baumann MH, Rothman RB, Mello NK, and Blough BE in April 2009, titled “Selective suppression of cocaine- versus food-maintained responding by monoamine releasers in rhesus monkeys: benzylpiperazine, (+)phenmetrazine, and 4-benzylpiperidine,” the researchers investigated the effects of various monoamine releasers, including 4-benzylpiperidine, on responding behaviors in rhesus monkeys. The study aimed to discern the differential impact of these substances on cocaine-maintained versus food-maintained responses, shedding light on their potential as treatments for cocaine addiction. (DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.143701)
- Arai Y, Hamamichi N, and Kinemuchi H conducted research in October 1986, titled “Time-dependent inhibition of rat brain monoamine oxidase by an analogue of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.” In this study, the scientists explored the time-dependent inhibition of rat brain monoamine oxidase by an MPTP analogue, 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine, providing insights into the biochemical interactions of these compounds. (DOI: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90473-8)
- Hoshikawa T and Inoue M, in their 2013 research, “Photoinduced direct 4-pyridination of C(sp3)–H Bonds,” investigated a novel chemical reaction. They explored the photoinduced direct 4-pyridination of C(sp3)–H bonds, demonstrating the potential of this reaction for organic synthesis. (DOI: 10.1039/c3sc51080h)
- In the realm of organic synthesis, Siegel S provided valuable information in 2001 through the work titled “Rhodium on alumina.” This work is featured in the e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. It discusses the use of rhodium on alumina as a reagent, highlighting its applications and contributions to organic chemistry. (DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rr003)