Contents
Summary
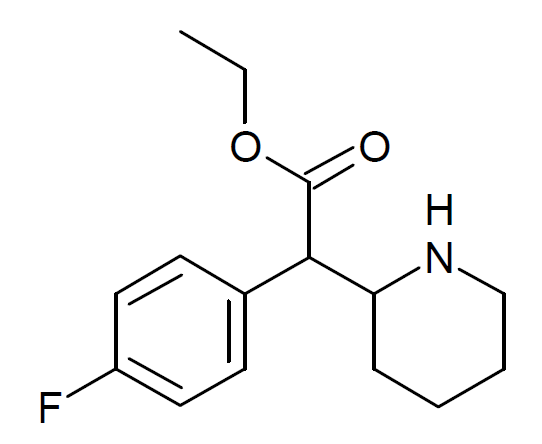
4-Fluoroethylphenidate, often abbreviated as 4-FEP, is a synthetic psychoactive compound that falls within the substituted phenidate class. It is structurally related to methylphenidate, which is a commonly prescribed medication for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). 4-FEP is known for its stimulating properties and potential for recreational use, though it is important to note that its safety profile and legal status vary by region.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 2160555-59-7 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 123133727 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H20FNO2 |
| Molar mass | 265.328 g·mol−1 |
Effects
The effects of 4-fluoroethylphenidate can be similar to those of other stimulants, including increased alertness, enhanced concentration, and elevated mood. Users may experience heightened energy levels and improved cognitive function. However, it is worth mentioning that along with these desired effects, 4-FEP can also induce undesirable side effects such as anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Some individuals may misuse it to achieve euphoria or a sense of invincibility, leading to potential addiction and other health risks.
Dosage
Determining a safe and appropriate dosage for 4-fluoroethylphenidate is challenging due to its limited research and varying purity levels in street drugs. Individuals who misuse 4-FEP often resort to experimentation, which is highly dangerous. It is crucial to emphasize that self-administered dosages can significantly differ from what might be considered safe, and there is a significant risk of overdose or adverse reactions.
Toxicity
The toxicity of 4-fluoroethylphenidate remains a subject of concern. Limited scientific research has been conducted to assess its long-term effects on human health comprehensively. However, like other stimulants, it can lead to cardiovascular issues, including increased heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, the compound’s potential for addiction and psychological side effects like anxiety and paranoia should not be underestimated.
Legal Status
The legal status of 4-fluoroethylphenidate varies significantly by country and jurisdiction. In some regions, it may be classified as a controlled substance, making its production, sale, and possession illegal. In other areas, it may exist in a legal gray area, not explicitly regulated due to its relatively recent emergence. Individuals should be aware of and adhere to the local laws and regulations governing the use of 4-FEP.
Pharmacology
4-Fluoroethylphenidate acts as a stimulant by increasing the availability of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. This increased neurotransmitter activity contributes to the heightened alertness and concentration observed in users. However, this artificial stimulation can lead to a range of side effects and potential long-term consequences, mainly when abused or misused.
Chemistry
Chemically, 4-fluoroethylphenidate is a derivative of phenidate, sharing structural similarities with methylphenidate (Ritalin). It is classified as a substituted phenolate, with a fluorine atom and an ethyl group added to the phenidate structure. The chemical structure of 4-FEP affects its interactions with neurotransmitter receptors in the brain, which, in turn, influences its psychoactive properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 4-fluoroethylphenidate is a synthetic psychoactive compound with stimulant effects that make it appealing to some individuals seeking enhanced alertness and cognitive performance. However, its misuse poses significant risks to health and well-being, including the potential for addiction and adverse psychological effects. The legality of 4-FEP varies by region, and individuals need to stay informed about the regulations in their area.
Given the limited research on 4-Fluoroethylphenidate’s safety and long-term effects, it is crucial to exercise caution and avoid its use outside of legitimate medical contexts. Its potential for harm far outweighs any perceived short-term benefits. Individuals with concerns about substance use should seek guidance from healthcare professionals and rely on evidence-based treatments and therapies rather than resorting to experimental and potentially dangerous substances.
FAQ
1. What is 4-Fluoroethylphenidate (4-FEP)?
- 4-Fluoroethylphenidate is a synthetic psychoactive compound with stimulant properties. It is chemically related to methylphenidate (Ritalin) and is known for its potential use as a stimulant drug.
2. What are the effects of 4-fluoroethylphenidate?
- The effects of 4-FEP can include increased alertness, enhanced concentration, elevated mood, and heightened energy levels. However, it may also lead to anxiety, restlessness, insomnia, and other undesirable side effects.
3. Is 4-fluoroethylphenidate safe to use?
- The safety of 4-FEP is a subject of concern, as there is limited research on its long-term effects. It has the potential for addiction, cardiovascular issues, and psychological side effects. It is not recommended for recreational use.
4. What is the recommended dosage for 4-fluoroethylphenidate?
- Determining a safe dosage for 4-FEP is challenging due to variations in purity and the lack of established guidelines. Self-administered dosages can be highly dangerous and should be avoided.
5. What are the potential risks of 4-fluoroethylphenidate use?
- Potential risks include addiction, increased heart rate and blood pressure, anxiety, paranoia, and other psychological side effects. Overdose is also a significant concern.
6. Is 4-fluoroethylphenidate legal?
- The legal status of 4-FEP varies by country and jurisdiction. It may be classified as a controlled substance in some areas, while in others, it may exist in a legal gray area. It is essential to be aware of local laws and regulations.
7. Can 4-fluoroethylphenidate be used for medical purposes?
- 4-FEP is not approved for medical use and is not prescribed by healthcare professionals. It lacks the safety and efficacy data required for medical treatments.
8. How does 4-fluoroethylphenidate work in the body?
- 4-FEP acts as a stimulant by increasing the availability of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. This leads to heightened alertness and cognitive performance.
9. What is the chemical structure of 4-fluoroethylphenidate?
- Chemically, 4-FEP is a derivative of phenidate, with a fluorine atom and an ethyl group added to the structure. Its chemical structure affects its psychoactive properties.
10. Are there any legitimate uses for 4-fluoroethylphenidate? – No, 4-FEP is not used for legitimate medical purposes. Its use is primarily associated with recreational drug use, although this is discouraged due to its potential risks.
11. What should I do if I have concerns about substance use, including 4-fluoroethylphenidate? – If you have concerns about substance use, it is advisable to seek guidance from healthcare professionals or addiction specialists. Evidence-based treatments and therapies are available to address substance use disorders.
12. How can I stay informed about the legal status of 4-fluoroethylphenidate in my area? – To stay informed about the legal status of 4-FEP, you can consult local drug enforcement agencies, government websites, or legal resources specific to your region. It is essential to be aware of and abide by local laws and regulations.
References
- In the “EMCDDA–Europol 2016 Annual Report on the implementation of Council Decision 2005/387/JHA,” jointly published by Europol and the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), comprehensive insights into the status and trends of drug-related issues are provided. This report offers a valuable resource for understanding drug-related challenges and strategies in Europe.
- Zaami S, Tagliabracci A, Berretta P, Busardò FP, and Marinelli E discussed the “Use of Methylphenidate Analogues as Cognitive Enhancers” in a 2019 article published in Frontiers in Psychiatry. This paper delves into the use of methylphenidate analogs for cognitive enhancement, exploring the ethical concerns surrounding this practice and its potential implications. (DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.01006)
- “The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Amendment) Order 2017” is a crucial document from the Government of the United Kingdom. This order represents legislative changes made to the Misuse of Drugs Act in 2017, reflecting the evolving landscape of drug control policies in the UK.
- The “Ordinance amending the Ordinance (1999:58) banning certain products that are harmful to health. Notification Number: 2021/241/S” is a significant regulation outlined in the Swedish Code of Statutes. It pertains to the ban on specific health-harmful products and serves as an essential legal instrument in the context of public health and safety.