Summary
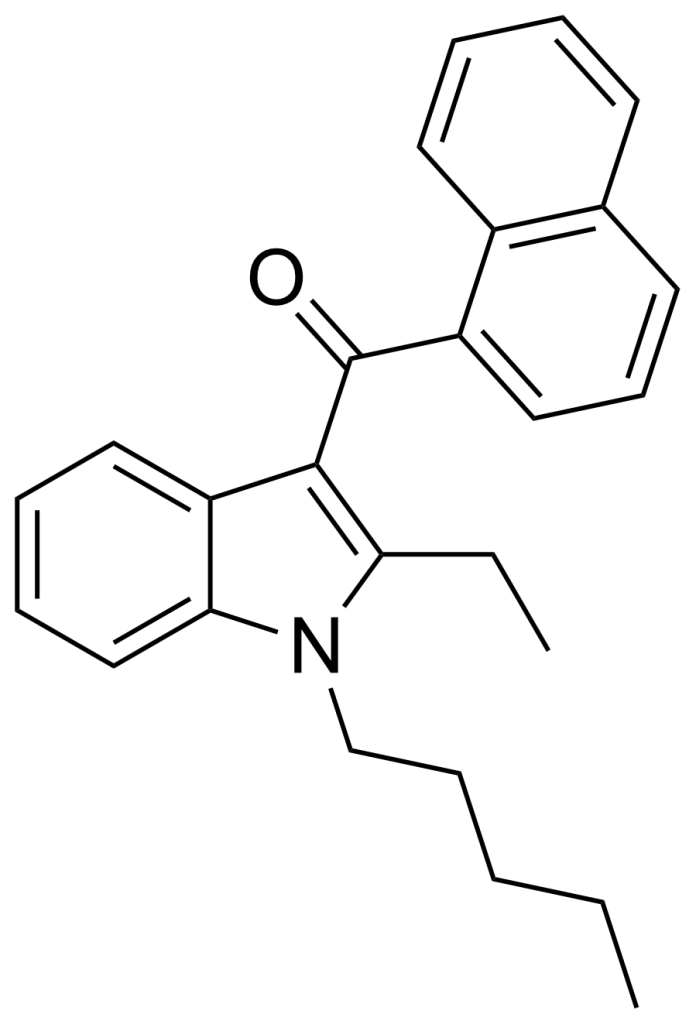
JWH-116, a member of the naphthoylindole family, is a synthetic ligand that interacts with cannabinoid receptors. It represents the indole 2-ethyl variant of its closely related compound, JWH-018. JWH-116 exhibits a binding affinity for the CB1 receptor with a reported Ki value of approximately 52 ± 5 nM.
In the United States, JWH-116, like other CB1 receptor agonists within the 3-(1-naphthyl)indole class, is categorized as a Schedule I Controlled Substance.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 619294-64-3 |
|---|---|
| ChemSpider | 29341485 |
| UNII | RKP962UAI3 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID60210966 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H27NO |
| Molar mass | 369.508 g·mol−1 |
FAQ
1. What is JWH-116?
JWH-116 is a synthetic compound belonging to the naphthoylindole family. It is a synthetic ligand that interacts with cannabinoid receptors in the body.
2. How does JWH-116 work?
JWH-116 operates by binding to and influencing the activity of cannabinoid receptors, particularly the CB1 receptor. This interaction can lead to various physiological and psychoactive effects.
3. What is the binding affinity of JWH-116 for the CB1 receptor?
The binding affinity of JWH-116 for the CB1 receptor is reported with a Ki (inhibition constant) value of approximately 52 ± 5 nM. This value provides insight into its potency in interacting with the CB1 receptor.
4. Is JWH-116 legal in the United States?
No, JWH-116 is classified as a Schedule I Controlled Substance in the United States. This means it is considered illegal and subject to strict regulation due to its potential for misuse and harm.
5. What are the potential effects of JWH-116?
JWH-116’s effects can be similar to those of natural cannabinoids and may include altered mood, relaxation, and changes in perception. However, the use of synthetic cannabinoids like JWH-116 can also have unpredictable and harmful side effects.
6. Is JWH-116 used for medical purposes?
JWH-116 has not been approved for any medical use. Its safety and efficacy for medical applications have not been established through rigorous testing and research. For medical conditions, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals and use approved medications.
7. Are there any risks associated with JWH-116 use?
Yes, there are risks associated with JWH-116 use, including potential health risks and legal consequences. The use of synthetic cannabinoids can lead to unpredictable and harmful side effects, making it unsafe and discouraged.
8. Where can I find more information about JWH-116?
To learn more about JWH-116, it is advisable to consult reputable scientific literature and healthcare professionals. It’s essential to prioritize safety and well-being and adhere to local laws and regulations regarding the use of controlled substances.
References
- Aromatic Stacking Interactions with CB(1) Receptor (February 2003): A study conducted by Huffman JW, Mabon R, Wu MJ, Lu J, Hart R, Hurst DP, and others in February 2003 investigates 3-Indolyl-1-naphthylmethanes, a class of cannabimimetic indoles. The research provides evidence for aromatic stacking interactions with the CB(1) cannabinoid receptor. This insight contributes to our understanding of the mechanisms behind the interaction of cannabinoids with their receptors.
- United States Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. § 812): The United States Controlled Substances Act, specifically outlined in Section 21 U.S.C. § 812, establishes the schedules of controlled substances in the United States. This legislative framework is essential for the classification and regulation of various substances, including those with potential psychoactive properties.