Summary
5,6-Methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-aminoindane, commonly referred to as MDMAI is a compound created in the 1990s by a research team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. In animal studies, it operates as a selective serotonin-releasing agent (SSRA) without neurotoxic effects, while in humans, it is believed to have the potential to act as an entactogen, enhancing feelings of emotional closeness and empathy.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 132741-82-3 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 125559 |
| ChemSpider | 111695 |
| UNII | 5N88M9ZTD8 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID20157742 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 191.230 g·mol−1 |
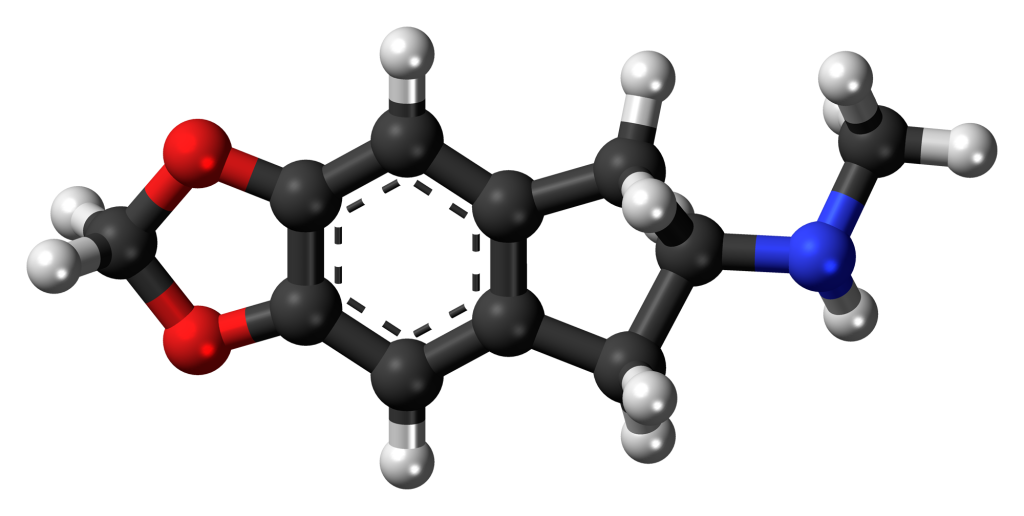
Chemistry
MDMAI can be conceptualized as a cyclic derivative of MDMA, where the alpha-methyl carbon of the alkylamino side chain reconnects to the 6-position of the aromatic ring, creating an indane ring structure. This transformation shifts the fundamental structure of the molecule from phenethylamine to aminoindane, resulting in significant differences in their pharmacological properties.
FAQ
1. What is MDMAI?
MDMAI, or 5,6-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-aminoindane, is a chemical compound that shares structural similarities with MDMA. It is a psychoactive substance that has been studied for its potential effects.
2. How does MDMAI compare to MDMA?
MDMAI can be considered a structural analog of MDMA, but it has distinct chemical differences. While MDMA is a phenethylamine, MDMAI belongs to the aminoindane class. These differences can lead to variations in their pharmacological properties.
3. Is MDMAI legal?
The legal status of MDMAI can vary from one region to another. It’s essential to check the laws and regulations specific to your area to determine its legality.
4. What are the potential effects of MDMA?
The specific effects of MDMAI have not been extensively studied. It is believed to act as an entactogen, potentially enhancing feelings of empathy and emotional closeness, but more research is needed to understand its effects fully.
5. Is MDMAI safe to use?
Due to limited research on its safety and effects, it is challenging to make definitive statements about the safety of MDMAI. Like with any psychoactive substance, using it carries risks, and caution is advisable.
6. Can MDMAI be detected in drug tests?
The detectability of MDMAI in drug tests may depend on the specific test used and its substances screened for. It is advisable to be aware of potential testing implications when considering its use.
7. What should I do if I suspect someone is using MDMAI or a similar substance?
If you suspect someone is using psychoactive substances or experiencing substance abuse issues, encourage them to seek professional help and support. Reach out to healthcare providers, counselors, or addiction specialists for guidance.
8. Are there harm reduction strategies for using substances like MDMAI safely?
Harm reduction strategies are essential when dealing with psychoactive substances. Prioritize safety, informed decision-making, and responsible use. Seek guidance from harm reduction organizations or healthcare professionals to minimize risks when using substances like MDMAI.
9. Where can I find more information about MDMAI?
For reliable information on MDMAI and similar compounds, consult reputable sources, scientific literature, government health agencies, and harm reduction organizations. Stay informed and make responsible choices.
10. Is there ongoing research on MDMAI?
Research on MDMAI may be ongoing. To access the latest information and developments, consult scientific literature, and sources focused on the study of psychoactive substances.