Summary
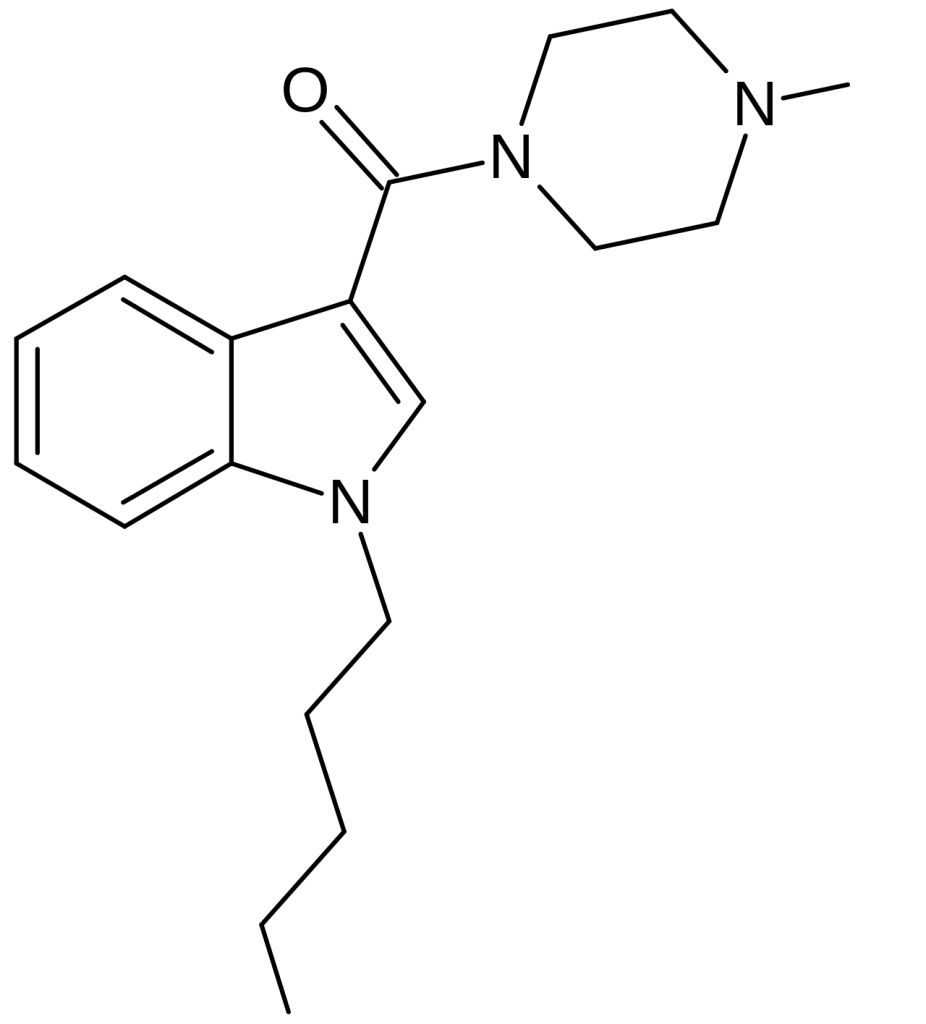
MEPIRAPIM, classified as an indole-based cannabinoid, distinguishes itself from JWH-018 by featuring a 4-methylpiperazine group instead of the naphthyl group. This compound has found applications as a critical component in synthetic cannabis products. Its discovery dates back to 2013, when it was initially recognized in Japan alongside FUBIMINA. It’s worth noting that MEPIRAPIM primarily functions as a T-type calcium channel inhibitor and exhibits minimal activity at the central CB1 receptor.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 2365542-29-4 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 101896603 |
| ChemSpider | 52085735 |
| UNII | W6OZW1T05K |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H27N3O |
| Molar mass | 313.445 g·mol−1 |
Legality
On November 10, 2014, Sweden’s public health agency recommended categorizing MEPIRAPIM as a hazardous substance.
FAQ
1. What is MEPIRAPIM?
MEPIRAPIM is an indole-based cannabinoid with a distinct chemical structure. It has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products.
2. How does MEPIRAPIM differ from JWH-018?
MEPIRAPIM sets itself apart from JWH-018 by incorporating a 4-methylpiperazine group instead of the naphthyl group, resulting in a unique chemical composition.
3. Where was MEPIRAPIM first identified?
MEPIRAPIM was initially recognized in Japan in 2013. It was discovered alongside another substance called FUBIMINA.
4. What are the primary effects of MEPIRAPIM?
MEPIRAPIM primarily functions as a T-type calcium channel inhibitor. Notably, it exhibits only minimal activity at the central CB1 receptor, which is associated with the effects of traditional cannabinoids.
5. Why was MEPIRAPIM suggested to be classified as a hazardous substance?
On November 10, 2014, Sweden’s public health agency recommended classifying MEPIRAPIM as a hazardous substance due to concerns about its potential health risks and safety implications.
6. Is MEPIRAPIM legal for use or sale?
The legal status of MEPIRAPIM may vary by region. It is essential to check local regulations and laws to determine their legality in your area.
7. Are there any health concerns associated with MEPIRAPIM use?
As with many synthetic cannabinoids, there are potential health risks and concerns related to the use of MEPIRAPIM. It is advised to avoid its use and be aware of associated health issues.
8. Where can I find more information about MEPIRAPIM?
You can access more information about MEPIRAPIM from reliable sources, including government health agencies and substance abuse prevention resources. Staying informed is crucial to understanding the potential risks and consequences associated with this substance.
References
- For comprehensive information on MEPIRAPIM, you can refer to Cayman Chemical, where details about this indole-based cannabinoid can be found. The data was retrieved on June 23, 2015.
- In a study by Uchiyama and colleagues in January 2014, two new synthetic cannabinoids, AM-2201 benzimidazole analog (FUBIMINA) and (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)(1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone (MEPIRAPIM), were identified in illegal products. The research is documented in Forensic Toxicology.
- Recent research published in May 2022 by Kevin and collaborators explored putative synthetic cannabinoids like MEPIRAPIM and 5F-BEPIRAPIM (NNL-2) as T-type calcium channel (CaV3) inhibitors. This study was featured in ACS Chemical Neuroscience.
- Information about the potential classification of cannabinoids as hazardous substances can be found under “Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara.” This update was retrieved on June 29, 2015.