Summary
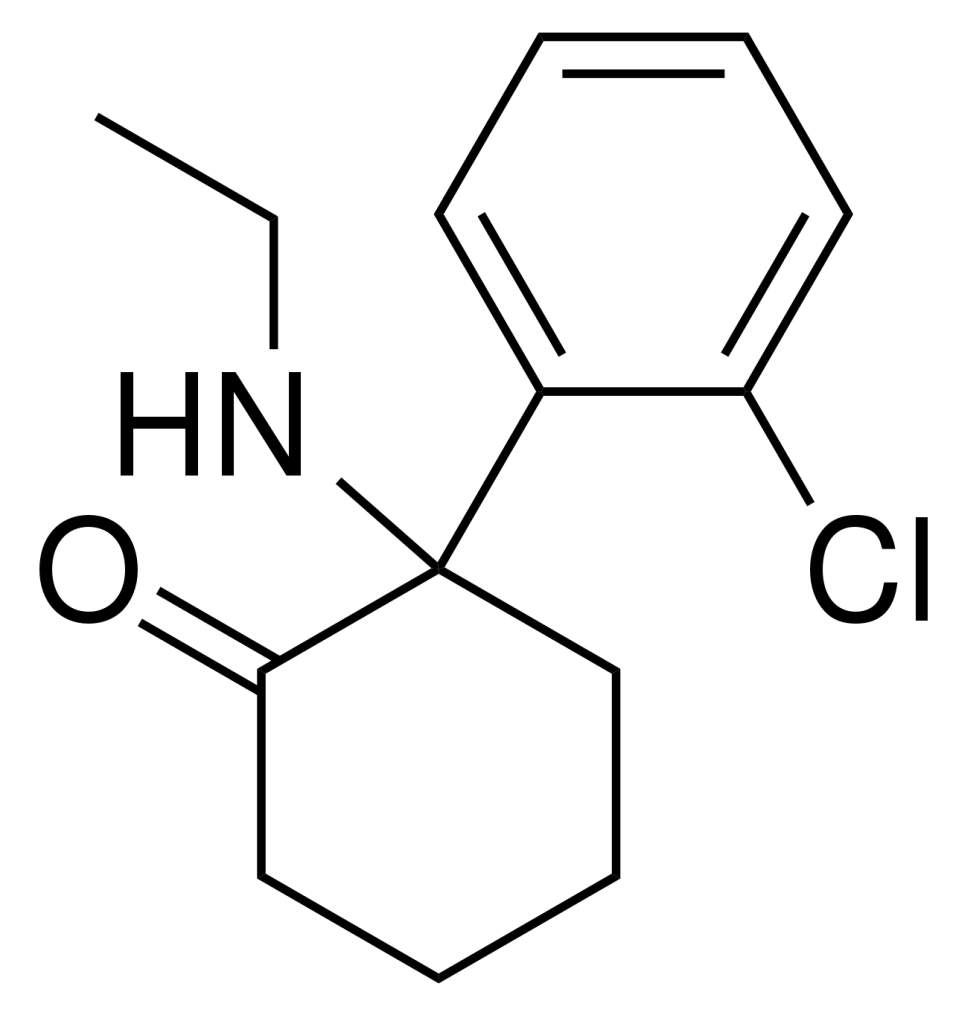
N-Ethylnorketamine, also known as eth ketamine, NENK, or 2-Cl-2′-Oxo-PCE, is a designer drug believed to share characteristics with ketamine. Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic drug recognized for its hallucinogenic and sedative effects. N-Ethylnorketamine emerged in online markets around September 2012 and has been detected in drug samples seized by analytical laboratories in the UK and various other European countries.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 1354634-10-8 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 57483649 |
| ChemSpider | 35805667 |
| UNII | TLL3802A3P |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H18ClNO |
| Molar mass | 251.75 g·mol−1 |
Legal Status
As of October 2015, N-Ethylnorketamine (NENK) has been classified as a controlled substance in several regions, including the United Kingdom, China, and the U.S. state of Alabama.
FAQ
1. What is N-Ethylnorketamine (NENK)?
N-Ethylnorketamine, commonly referred to as NENK, is a designer drug with properties resembling ketamine, which is known for its dissociative anesthetic, hallucinogenic, and sedative effects.
2. When was NENK first introduced to the market?
NENK began to emerge in online markets around September 2012, becoming accessible to individuals through various channels.
3. How is NENK used?
NENK is typically consumed through oral ingestion, similar to ketamine. However, the specific method of use can vary among individuals. It’s essential to note that the use of NENK can pose health risks and may be subject to legal restrictions in certain regions.
4. What are the effects of NENK?
NENK is believed to induce effects similar to ketamine, including altered sensory perception, sedation, and hallucinogenic experiences. The intensity and duration of these effects can vary based on factors like dosage and individual tolerance.
5. Is NENK safe for use?
The safety of NENK is not well-documented, and its recreational use is associated with potential health risks and adverse effects. As with many designer drugs, using NENK carries inherent risks, and its safety is not guaranteed.
6. Is NENK addictive?
The addictive potential of NENK is not extensively studied, but, like ketamine and similar substances, it may have the potential for psychological dependence, particularly with frequent or heavy use.
7. Is NENK legal?
The legal status of NENK varies by jurisdiction. It has been classified as a controlled substance in several regions, including the United Kingdom, China, and the U.S. state of Alabama. In other areas, regulations may vary, so it’s crucial to understand the legal status in your specific location.
8. How can one ensure their safety when dealing with NENK?
To prioritize safety, it’s essential to stay informed about local regulations, potential health risks, and the legal status of NENK in your region. Additionally, always exercise caution and moderation and seek guidance from healthcare professionals when considering the use of substances like NENK.
9. Where can I find reliable information about NENK?
For accurate and up-to-date information on N-Ethylnorketamine, consult trusted sources such as government health agencies, substance abuse prevention organizations, and medical professionals. Being well-informed is crucial when dealing with substances like NENK, considering the associated risks and legal implications.
References
- The Methoxetamine Report of 2012, provided by the Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD), offers valuable insights into the substance’s characteristics and potential risks.
- In July 2019, a study led by Sayson LV, along with a team of researchers, investigated novel methoxetamine analogs, specifically N-ethylnorketamine hydrochloride (NENK), 2-MeO-N-ethylketamine hydrochloride (2-MeO-NEK), and 4-MeO-N-ethylketamine hydrochloride (4-MeO-NEK). Their research revealed these analogs to have rapid antidepressant effects through the activation of AMPA and 5-HT2 receptors. This study was published in the journal Psychopharmacology, Volume 236, Issue 7, with the identifier doi:10.1007/s00213-019-05219-x.
- The Explanatory Memorandum to the Misuse of Drugs (1971) Amendment Order 2013 provides additional information about the regulatory framework surrounding the use and control of various substances.
- The “关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知” (in Chinese), issued by the China Food and Drug Administration on September 27, 2015, outlines guidelines and regulations related to the classification and control of non-medicinal psychoactive substances.
- In March 2014, the Alabama Senate Bill 333 introduced amendments to controlled substances regulations, including the inclusion of additional synthetic controlled substances and analogue substances. These changes are designed to address issues related to the trafficking of controlled substance analogues and also involve increasing the requisite weight for certain substances.