Summary
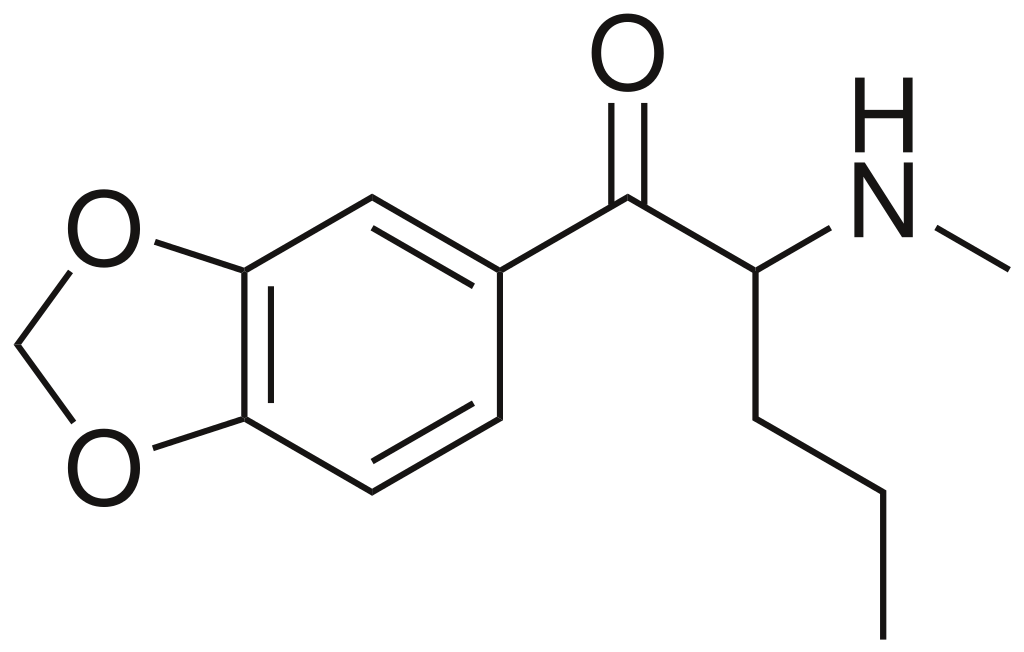
Pentylone, also known as β-Keto-Methylbenzodioxolylpentanamine, βk-Methyl-K, βk-MBDP, methylenedioxypentedrone, or 1‐(3,4‐methylenedioxyphenyl)‐2‐(methylamino)pentan‐1‐one, is a stimulant that was developed during the 1960s. This compound falls under the category of substituted cathinones, which are a type of substituted phenethylamines.
Pentylone has been detected in specific samples of powders that were marketed as “NRG-1.” These samples sometimes contained varying mixtures of other cathinone derivatives such as mephedrone, MDPBP, MDPV, and 4-MePPP. Additionally, Pentylone was found with 4-MePPP in products sold as “NRG-3.”
Reports suggest that using Pentylone may result in side effects such as heightened paranoia, agitation, and difficulty sleeping. At higher doses, these effects can persist for several days.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 698963-77-8 17763-01-8 (hydrochloride) |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 60208608 |
| ChemSpider | 29786041 |
| UNII | IGN39WGH0Q |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID401014183 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 235.283 g·mol−1 |
Pharmacology
Pentylone functions as a compound that inhibits the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, while also serving as an agent that releases serotonin.
Legality
Pentylone has been prohibited in several countries, including Canada, Germany, Sweden, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
FAQ
1. What is Pentylone?
Pentylone is a synthetic compound classified as a substituted cathinone, falling within the broader category of substituted phenethylamines. It is known for its stimulant properties.
2. How was Pentylone developed?
Pentylone was developed during the 1960s as a synthetic stimulant.
3. What are the shared names and synonyms for Pentylone?
Pentylone goes by various names and synonyms, including β-Keto-Methylbenzodioxolylpentanamine, βk-Methyl-K, βk-MBDP, methylenedioxypentedrone, and 1‐(3,4‐methylenedioxyphenyl)‐2‐(methylamino)pentan‐1‐one.
4. What are the effects of Pentylone use?
Pentylone is primarily known for its stimulant effects, including increased energy, alertness, and euphoria. However, it may also lead to side effects such as paranoia, agitation, and sleep disturbances, especially at higher doses.
5. Where has Pentylone been banned or prohibited?
Pentylone has been banned in several countries, including Canada, Germany, Sweden, the United States, and the United Kingdom.
6. Is Pentylone legal in any countries or regions?
The legal status of Pentylone varies by country and jurisdiction. It is essential to check the specific regulations and laws in your area regarding the use and possession of this compound.
7. What is the mechanism of action of Pentylone?
Pentylone acts as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor and a serotonin-releasing agent, affecting neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
8. Are there any known health risks associated with Pentylone use?
The use of Pentylone is associated with potential health risks, including side effects such as paranoia, agitation, and sleep disturbances. At higher doses, these effects may persist for several days. Additionally, the long-term health effects of Pentylone use are not well understood.
9. Where can I find more information about Pentylone?
Additional information about Pentylone can be found in scientific literature, drug awareness resources, and government publications on controlled substances. Always prioritize safety and legal compliance when seeking information about such compounds.
References
- Anvisa (2023-07-24). “RDC Nº 804 – Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial” [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 – Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). This official document, in Brazilian Portuguese, outlines regulatory control over substances, including Pentylone, in Brazil. [Accessed on: 2023-08-27]
- Brandt SD, Freeman S, Sumnall HR, Measham F, Cole J (September 2011). “Analysis of NRG ‘legal highs’ in the UK: identification and formation of novel cathinones”. This research published in Drug Testing and Analysis investigates novel cathinones, shedding light on substances related to Pentylone. [DOI: 10.1002/dta.204]
- GB 1085135, “Substituted phenyl-α-amino ketones.”, issued 1969. This patent describes substituted phenyl-α-amino ketones, providing insights into chemical compounds related to Pentylone.
- Bish J (4 August 2017). “Watch Out for Pentylone, the Horrible New MDMA Additive”. This article in Vice raises awareness about Pentylone, highlighting its emergence as an additive in MDMA.
- Simmler LD, Rickli A, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (April 2014). “Monoamine transporter and receptor interaction profiles of a new series of designer cathinones”. This scientific study in Neuropharmacology explores the interaction profiles of designer cathinones, including Pentylone. [DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.008]
- “Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara” [Cannabinoids are proposed to be classified as a health hazard]. This Swedish source discusses the classification of substances, including Pentylone, as health hazards. [Accessed on: 25 March 2015]
- “Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of 10 Synthetic Cathinones Into Schedule I”. This U.S. Federal Register document by the Drug Enforcement Administration addresses the temporary placement of synthetic cathinones, which includes Pentylone, into Schedule I.