Contents
Summary
Sufentanil, or sufentanyl, marketed under the brand name Sufenta, is an exceptionally potent synthetic anilidopiperidine opioid analgesic. It boasts rapid onset and a brief duration of action, making it a valuable tool in the medical field for pain management during surgical procedures and post-operative recovery. Regarding potency, Sufentanil surpasses pharmaceutical-grade morphine by approximately 500 to 1,000 times and exceeds pharmaceutical-grade fentanyl by roughly 10 times. While the subjective effects of Sufentanil are akin to those of heroin, users often note a notably reduced euphoric “high” compared to heroin, along with heightened respiratory depression, sedation, and pain relief. In the realm of human medicine, Sufentanil stands as the most potent opioid analgesic currently available.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 56030-54-7 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 41693 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 3534 |
| DrugBank | DB00708 |
| ChemSpider | 38043 |
| UNII | AFE2YW0IIZ |
| KEGG | D05938 as salt: D00845 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:9316 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL658 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID6023604 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.168.858 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 386.55 g·mol−1 |
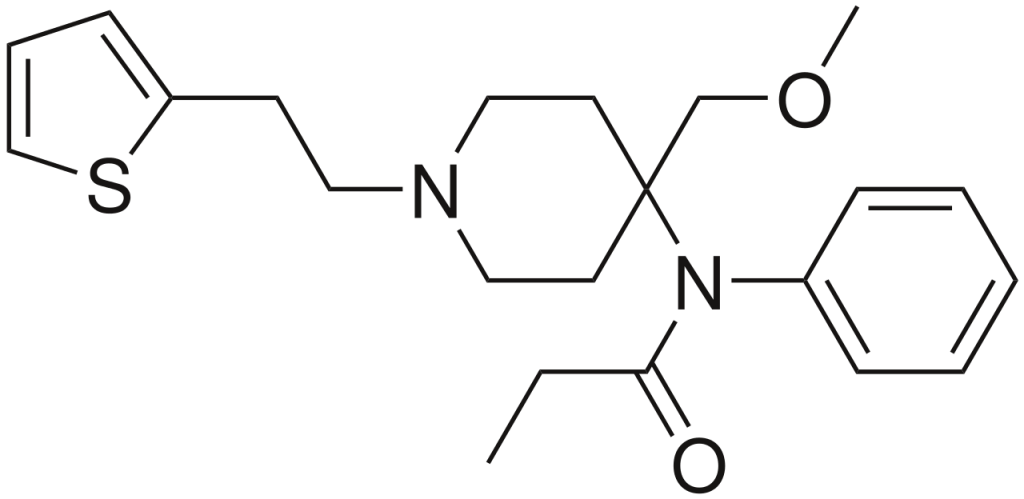
Chemistry
In the synthetic anilidopiperidine class, Sufentanil shares structural similarities with fentanyl and acetyl fentanyl. Replacing one phenyl group with a thiophene or thiofuran group in sufentanil’s structure is a notable distinction. It’s worth mentioning that thiophene groups can often substitute phenyl groups without substantially losing potency. Sufentanil’s empirical formula is C22H30N2O2S, possessing a molar mass of 386.552 grams per mole.
Sufentanil Citrate Injection, an opioid agonist, is available as a solution containing 50 mcg/mL equivalent of sufentanil base, with pH adjusted to fall within the range of 3.5 to 6.0. Its chemical name is N-[4-(methoxymethyl)-1-[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanolamine: 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1). The molecular weight of Sufentanil Citrate Injection is 578.68. This product is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, and preservative-free aqueous solution designed for intravenous or epidural administration.
Pharmacology
Understanding Sufentanil and its Effects
- Sufentanil, a synthetic anilidopiperidine, shares structural similarities with fentanyl and acetylfentanyl. Notably, it replaces one phenyl group with a thiophene or thiofuran group, a modification that often maintains potency. Sufentanil’s chemical formula is C22H30N2O2S, with a molar mass of 386.552 grams per mole.
- Sufentanil Citrate Injection, an opioid agonist, contains 50 mcg/mL of sufentanil base, with pH adjusted between 3.5 and 6.0. Its chemical name is N-[4-(methoxymethyl)-1-[2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanolamine: 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1). It possesses a molecular weight of 578.68. It is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, and preservative-free aqueous solution for intravenous or epidural administration.
Mechanism of Sufentanil and Safety Considerations
- The recreational effects of sufentanil stem from its structural resemblance to endogenous endorphins, which naturally activate μ-opioid receptors. This structural mimicry results in euphoria, pain relief, and anxiolytic effects, as endorphins are responsible for reducing pain, inducing sleepiness, and eliciting pleasure. Sufentanil, like endorphins, acts as an exceedingly potent μ-opioid agonist, yet it has an exceptionally short biological half-life of only 162 minutes.
- Due to its extreme potency, sufentanil finds frequent use in surgical procedures and post-operative pain management, particularly for patients with high opioid dependence or tolerance resulting from chronic pain or illicit opioid use. Sufentanil is the most potent opioid painkiller approved for human use, with medications stronger than sufentanil reserved solely for veterinary purposes. It is also utilized in surgical scenarios involving patients on high-dose buprenorphine for chronic pain, as it is the only opioid capable of displacing buprenorphine from central nervous system opioid receptors and providing analgesia.
Tolerance, Relapse, and Dangerous Interactions
- Tolerance to sufentanil’s effects develops over time, with varying rates for different products. Users may need increasing doses to achieve the same impact. After cessation, it takes about 3 to 7 days for tolerance to reduce by half and 1 to 2 weeks to return to baseline, assuming no further consumption. Sufentanil also exhibits cross-tolerance with other opioids, diminishing the effects of all opioids after its use.
- The risk of fatal opioid overdoses increases significantly after cessation and relapse due to reduced tolerance. To mitigate this, starting with a fraction of the usual dose is safer when relapsing. Environmental factors can influence opioid tolerance, as shown in a scientific study where rats with a history of heroin administration were more likely to overdose when given their dose in an unfamiliar environment.
Dangerous Interactions
- Combining psychoactive substances can be perilous. The following interactions should be approached with caution:
- Alcohol: Potentiates sedation and ataxia, leading to potential unconsciousness.
- Amphetamines: Stimulants increase respiration rate, potentially causing respiratory arrest when opioids wear off.
- Benzodiazepines: Strongly potentiates central nervous system and respiratory depression, leading to unconsciousness and blackouts.
- Cocaine: Stimulants increase opioid dosing potential, posing a risk of respiratory arrest when the stimulant effects diminish.
- DXM: Generally considered toxic, it can lead to CNS depression, breathing difficulties, heart issues, and liver toxicity.
- GHB/GBL: Potentiate each other unpredictably, increasing the risk of unconsciousness and vomit aspiration.
- Ketamine Carries a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness, with a severe aspiration risk if users become unconscious.
- MAOIs May cause severe adverse reactions when combined with opioids, leading to agitation, seizures, and coma.
- MXE: Can potentiate opioid effects but also increases the risk of respiratory depression and organ toxicity.
- Nitrous: Potentiates ataxia and sedation, possibly leading to unconsciousness and vomit aspiration.
- PCP: May reduce opioid tolerance, increasing overdose risk.
- Tramadol: Increases the risk of seizures and combines with other opioids to enhance CNS and respiratory depression.
- Grapefruit: Affects opioid metabolism, potentially prolonging drug effects and increasing toxicity.
Legal status
- Germany: Sufentanil is categorized as a controlled substance under Anlage III of the BtMG and can solely be prescribed using a narcotic prescription form.
- Russia: Sufentanil is a Schedule II controlled substance in Russia.
- Switzerland: Sufentanil is recognized as a controlled substance, listed explicitly under Verzeichnis A. Medicinal use is allowed within Switzerland.
- United States: Sufentanil is classified as a Schedule II Controlled Substance by the Controlled Substances Act in the United States.
FAQ
- What is Sufentanil?
- Sufentanil is a highly potent synthetic opioid analgesic. It is used medically for pain management during surgical procedures and post-operative recovery.
- How does Sufentanil work?
- Sufentanil works by binding to and activating μ-opioid receptors in the central nervous system. This activation leads to pain relief, sedation, and other opioid-related effects.
- How potent is Sufentanil compared to other opioids?
- Sufentanil is approximately 500 to 1,000 times more potent than pharmaceutical-grade morphine and about 10 times more potent than pharmaceutical-grade fentanyl.
- What are the medical uses of Sufentanil?
- Sufentanil is primarily used in surgical settings to provide analgesia and manage pain during and after surgery. It is precious in cases where patients have a high tolerance to opioids due to chronic pain or prior opioid use.
- Are there recreational effects associated with Sufentanil?
- Yes, Sufentanil can produce euphoria, sedation, and pain relief, similar to other opioids. However, it is essential to note that the recreational use of Sufentanil is hazardous due to its potency.
- Is Sufentanil addictive?
- Like other opioids, Sufentanil has a high potential for addiction, especially with chronic use. Users can develop physical and psychological dependence on the drug.
- What is opioid tolerance, and how does it relate to Sufentanil use?
- Opioid tolerance refers to the reduced effectiveness of opioids over time, requiring higher doses to achieve the same pain relief or euphoria. Sufentanil use can lead to tolerance, necessitating dose escalation for desired effects.
- What are the potential dangers of Sufentanil use?
- Sufentanil use carries risks of respiratory depression, overdose, and addiction. Combining Sufentanil with other substances, especially depressants like alcohol or benzodiazepines, can be life-threatening.
- Is Sufentanil legal?
- Sufentanil’s legal status varies by country. It is a controlled substance in many places and can only be obtained with a prescription. Always follow local laws and regulations.
- What precautions should I take when using Sufentanil medically or recreationally?
- If using Sufentanil under medical supervision, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully. It is strongly discouraged regarding recreational use due to its high risk of harm and addiction. Never combine Sufentanil with other substances without consulting a healthcare professional, as it can lead to dangerous interactions.
- What should I do in case of a Sufentanil overdose or adverse reaction?
- In an overdose or adverse reaction, seek immediate medical attention. Sufentanil overdose can be life-threatening, and professional medical help is essential.
- Is there a safe way to discontinue Sufentanil use?
- Discontinuing Sufentanil use should be done under medical supervision. Abruptly stopping opioid use can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which can be managed with medical guidance.
- Can Sufentanil be used for chronic pain management?
- Sufentanil can be used for chronic pain management in some instances, but it should only be prescribed and administered by a qualified healthcare provider with experience in pain management.
- Is Sufentanil available in different forms?
- Sufentanil is commonly available in injectable forms for medical use. It is not typically available in oral forms for outpatient use.
- Where can I find more information about Sufentanil?
- For detailed information about Sufentanil, consult healthcare professionals, pharmacists, or trusted medical sources. Always prioritize your health and safety when considering the use of any medication.
References
- Understanding the Dangers of Depressant Combinations – Exploring the risks associated with combining depressant substances and the potential consequences of such interactions.
- Official Information on Sufentanil – Accessing comprehensive details about Sufentanil, its uses, and safety information via Drugs.com.
- Insights from a 1982 Study on Heroin Overdose – Examining a study from 1982 that delves into the factors contributing to heroin overdose deaths, shedding light on environmental cues.
- Opioid Toxidrome Triggered by Grapefruit Juice and Methadone – Discovering a study from March 2020 that investigates the development of opioid toxidrome following the consumption of grapefruit juice in the context of methadone maintenance.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors, Opioid Analgesics, and Serotonin Toxicity – Exploring the relationship between monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), opioid painkillers, and serotonin toxicity, as discussed in a 2005 article.
- German Legal Classification of Sufentanil – Understanding the legal status of Sufentanil in Germany, where it is classified under Anlage III BtMG.
- Russian Government Resolution on Sufentanil – Gaining insights into the official stance on Sufentanil in Russia through a government resolution dated October 1, 2012, with revisions as of August 9, 2019.
- Swiss Regulations on Controlled Substances – Accessing information on the control and regulation of substances, including Sufentanil, in Switzerland, as outlined in the “Verordnung des EDI über die Verzeichnisse der Betäubungsmittel, psychotropen Stoffe, Vorläuferstoffe und Hilfschemikalien.”
- United States Controlled Substances Classification – Reviewing the classification of Sufentanil as a controlled substance in the United States according to the DEA’s Controlled Substances Act.