Contents
Summary
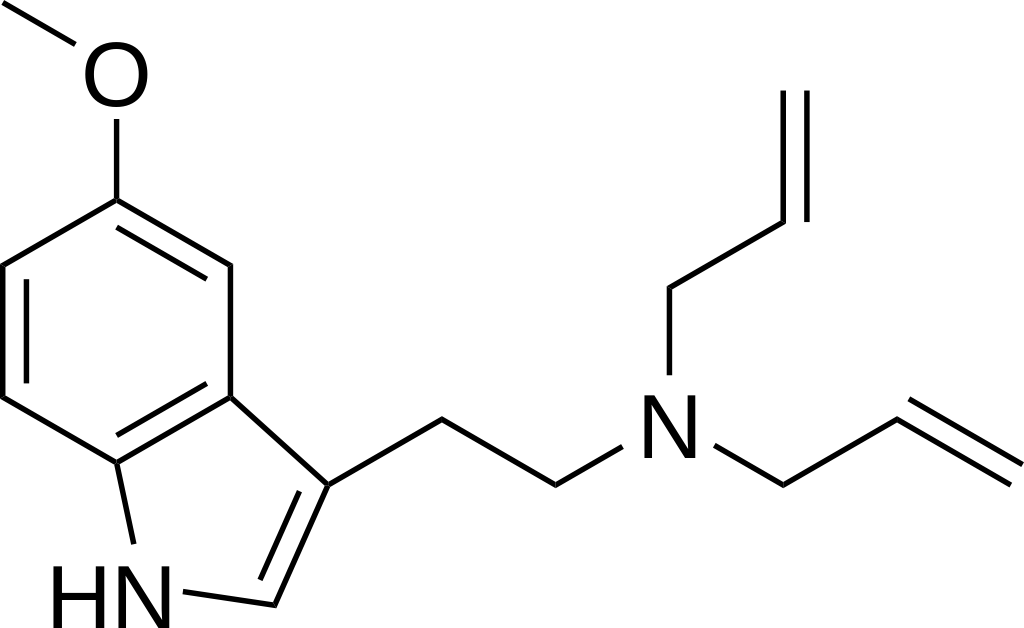
5-MeO-DALT, also known as N,N-di allyl-5-methoxy tryptamine, is a psychedelic tryptamine compound that was initially synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| CAS Number | 928822-98-4 |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | 50878551 |
| ChemSpider | 21106245 |
| UNII | V25VK0QTAA |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2391541 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID30239169 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 270.376 g·mol−1 |
Chemistry
The chemical is formally known as N-allyl-N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl] prop-2-en-1-amine and shares structural similarities with 5-MeO-DPT and DALT.
In April 2020, Chadeayne and colleagues successfully determined the crystal structure of the freebase variation of 5-MeO-DALT.
Pharmacology
| Binding site | pKi ± SEM at binding site |
| 5-HT1A | 7.70 ± 0.10 |
| 5-HT1B | 6.13 ± 0.04 |
| 5-HT1D | 7.00 ± 0.10 |
| 5-HT1E | 6.30 ± 0.05 |
| 5-HT2A | 6.66 ± 0.08 |
| 5-HT2B | 7.23 ± 0.05 |
| 5-HT2C | 6.34 ± 0.08 |
| 5-HT5A | 5.48 ± 0.04 |
| 5-HT6 | 6.81 ± 0.03 |
| 5-HT7 | 7.05 ± 0.07 |
| α2A | 6.67 ± 0.07 |
| α2B | 6.14 ± 0.04 |
| α2C | 5.83 ± 0.06 |
| H1 | 6.30 ± 0.06 |
| H3 | 5.77 ± 0.04 |
| κOR | 5.95 ± 0.07 |
| μOR | < 5.00 |
| σ1 | 6.52 ± 0.06 |
| σ2 | 6.60 ± 0.05 |
| DAT | 5.50 ± 0.20 |
| NET | < 5.00 |
| SERT | 6.30 ± 0.05 |
History
Alexander Shulgin dispatched the initial information on the synthesis and effects of 5-MeO-DALT to a research associate named Murple in May 2004. Subsequently, this information was disseminated online. In June 2004, 5-MeO-DALT became accessible through internet research chemical vendors as it was synthesized by commercial laboratories in China. By August 2004, both the synthesis and effects of 5-MeO-DALT were documented and published by Erowid.
Therapeutic use
A wealth of anecdotal accounts and a preliminary small-scale trial suggest that 5-MeO-DALT holds promise for alleviating cluster headaches, which are renowned as one of the most agonizing medical conditions. These findings align with existing evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of chemically-related indoleamines in addressing cluster headaches.
Side effects
There is no published literature on the toxicity of 5-MeO-DALT.
Legal Status
China:
As of October 2015, 5-MeO-DALT is classified as a controlled substance in China.
Japan:
In Japan, 5-MeO-DALT was designated as a controlled substance starting in April 2007, following an amendment to the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law.
United Kingdom:
5-MeO-DALT was reclassified as a Class A drug in the United Kingdom on January 7, 2015, as a result of an update to the tryptamine blanket ban.
Singapore:
5-MeO-DALT is included in the Fifth Schedule of the Misuse of Drugs Act (MDA), rendering it illegal in Singapore since May 2015.
Sweden:
Sweden’s Riksdag added 5-MeO-DALT to schedule I, which covers substances, plant materials, and fungi that typically lack medical applications, on May 1, 2012. The Medical Products Agency published this in their regulation LVFS 2012:6, listed as 5-MeO-DALT N-allyl-N-[2-(5-metoxi-1H-indol-3-yl)etyl]-prop-2-en-1-amin.
United States:
At the federal level in the United States, 5-MeO-DALT has yet to be officially scheduled. However, it could potentially be treated as an analog of 5-Meo-DiPT, which is a controlled substance in the USA, or an analog of another tryptamine, making purchase, sale, or possession subject to prosecution under the Federal Analog
Florida:
In the state of Florida, 5-MeO-DALT is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance, making it illegal to buy, sell, or possess in Florida.
Louisiana:
Similarly, in the state of Louisiana, 5-MeO-DALT is designated as a Schedule I controlled substance, rendering it illegal to buy, sell, or possess in Louisiana.
Notes
- Anvisa (The National Health Surveillance Agency) in Brazil issued Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 on July 24, 2023. This resolution pertains to the Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control. The official publication was made in the Diário Oficial da União on July 25, 2023, with archived records available until August 27, 2023.
- In April 2020, Chadeayne and colleagues conducted research on the freebase form of 5-MeO-DALT, with their findings published in IUCrData, a publication of the International Union of Crystallography (IUCr). This study advanced our understanding of N,N-diallyl-5-meth-oxy-tryptamine.
- Cozzi and Daley’s research, published in February 2016 in “Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,” delved into receptor binding profiles and quantitative structure-affinity relationships of certain 5-substituted-N,N-diallyltryptamines.
- In October 2015, Michely and colleagues conducted a study focusing on the metabolism and detectability of N,N-diallyltryptamine (DALT) and 5-methoxy-DALT in urine. Their findings were documented in “Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.”
- In a study published in January 2016, Dinger, Woods, Brandt, Meyer, and Maurer explored the cytochrome P450 inhibition potential of new psychoactive substances from the tryptamine class. Their findings were featured in “Toxicology Letters.”
- An interview with Alexander Shulgin conducted by Morris and Smith, provides insights into the mind of the renowned chemist, shedding light on various substances including 5-MeO-DALT.
- Additional insights on 5-MeO-DALT and related compounds can be found in Sasha Shulgin’s discussions, available via YouTube.
- Post’s patient surveys from 2015 and 2014 investigated the treatment of cluster headache symptoms using synthetic tryptamines like 5-MeO-DALT, providing valuable data on the subject.
- Research by Brandt and colleagues, published in February 2020, delves into pharmacotherapy for cluster headaches, offering potential treatment options.
- The study conducted by Schindler, Gottschalk, Weil, Shapiro, Wright, and Sewell, published on October 20, 2015, explores the use of indoleamine hallucinogens in cluster headache, providing insights into their effects and effectiveness.
- The China Food and Drug Administration issued a notification regarding the classification of non-medical narcotics and psychotropic substances on September 27, 2015.
- In Japan, an update on unapproved and unlicensed medicines was released on July 24, 2015, revealing new regulations.
- Singapore’s Central Narcotics Bureau (CNB) shared a news release on April 30, 2015, discussing controlled substances.
- In Sweden, changes were made to the regulation regarding narcotics by the Medical Products Agency on April 20, 2012.
- The Controlled Substances Act in the United States provides guidelines regarding controlled substances and their scheduling, including substances like 5-MeO-DALT.
- In Florida, 5-MeO-DALT was classified as a Schedule I controlled substance, making its purchase, sale, or possession illegal.
- The state of Louisiana also designated 5-MeO-DALT as a Schedule I controlled substance, rendering it illegal to buy, sell, or possess within the state.