Summary
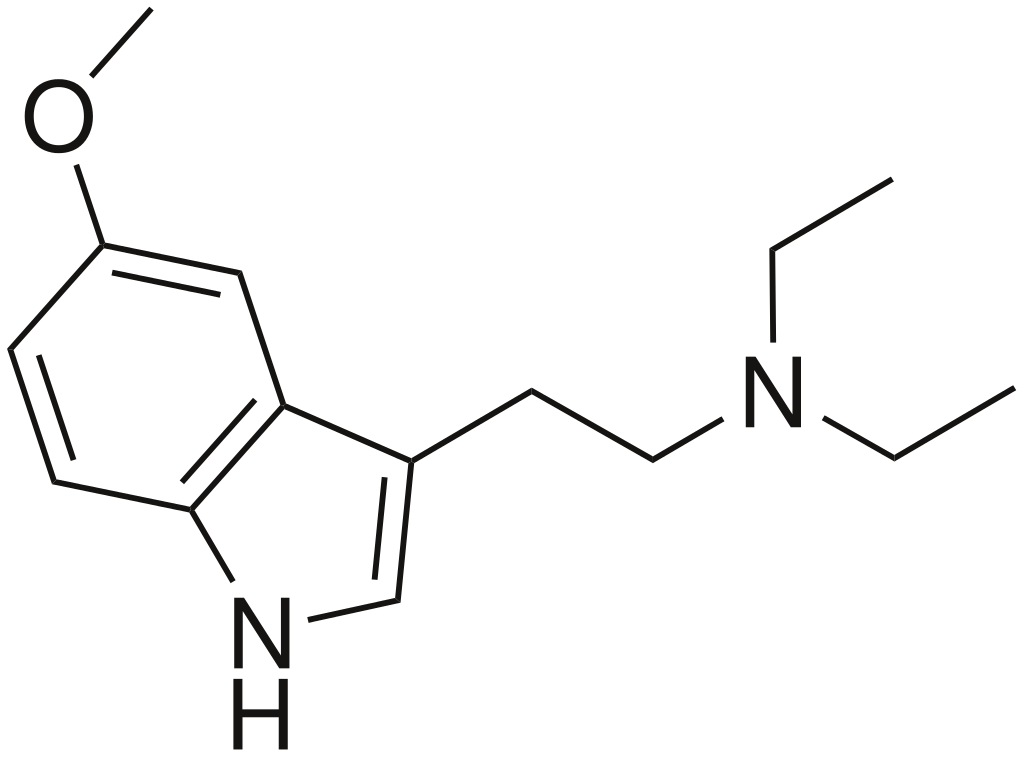
5-MeO-DET, also known as 5-methoxy-N,N-diethyltryptamine, is a hallucinogenic tryptamine compound.
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2454-70-8 |
| PubChem CID | 417608 |
| ChemSpider | 369669 |
| UNII | LM6R54JKYE |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL342986 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID30329130 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 246.354 g·mol−1 |
Pharmacology
5-MeO-DET demonstrates an inhibition of serotonin reuptake with an IC50 value of 2.4 μM and activates 5-HT2A receptors with an EC50 value of 8.11 nM.
Effects
At low dosages (ranging from 0.5 to 1 mg), individuals have reported experiencing a relaxing body high along with mild entheogenic effects. However, Alexander Shulgin’s observations in TiHKAL indicate that higher dosages (typically in the range of 1 to 3 mg) can lead to significantly unpleasant reactions.

FAQ
1. What is 5-MeO-DET?
- 5-MeO-DET, or 5-methoxy-N, N-diethyltryptamine, is a psychedelic compound belonging to the tryptamine class known for its hallucinogenic effects.
2. How does 5-MeO-DET work?
- 5-MeO-DET primarily affects the serotonin system. It inhibits serotonin reuptake and activates 5-HT2A receptors in the brain.
3. What are the effects of 5-MeO-DET?
- At low doses (0.5–1 mg), users often report experiencing a relaxing body high and mild entheogenic effects. Higher doses (1–3 mg) can lead to more intense and potentially unpleasant reactions.
4. Is 5-MeO-DET legal?
- The legal status of 5-MeO-DET varies by country and jurisdiction. It’s essential to check the specific regulations in your area, as it may be considered a controlled or illegal substance in some places.
5. How is 5-MeO-DET typically consumed?
- 5-MeO-DET is often ingested orally in its powder or crystalline form. It can be taken as a standalone substance or in combination with other compounds.
6. What precautions should I take when using 5-MeO-DET?
- If you choose to use 5-MeO-DET, start with a low dose to gauge its effects on your body. Always use in a safe and controlled environment, preferably with a trusted friend or sitter. Be aware of the legal status in your location and prioritize your safety.
7. Are there any risks or side effects associated with 5-MeO-DET?
- The use of 5-MeO-DET can lead to various psychological and physiological effects. Higher doses can result in more pronounced and potentially negative reactions, so responsible use is crucial.
8. Can 5-MeO-DET be used for therapeutic purposes?
- Some individuals have explored the potential therapeutic benefits of 5-MeO-DET, but further research is needed to understand its safety and efficacy for such applications.
9. Where can I find more information about 5-MeO-DET?
- It’s essential to consult reputable sources for information about 5-MeO-DET, such as scientific publications, online forums, or educational websites. Always verify the legality and safety of any substance before use.
References
- Schulze-Alexandru M, Kovar KA, Vedani A (December 1999). “Quasi-atomistic Receptor Surrogates for the 5-HT2A Receptor: A 3D-QSAR Study on Hallucinogenic Substances.” This study explored the receptor surrogates for the 5-HT2A receptor through a 3D-QSAR analysis, shedding light on the structural properties of hallucinogenic compounds.
- Gatch MB, Forster MJ, Janowsky A, Eshleman AJ (July 2011). “Abuse liability profile of three substituted tryptamines.” This research delves into the abuse liability of various substituted tryptamines, providing insights into their potential for misuse.
- Glennon RA, Gessner PK (April 1979). “Serotonin receptor binding affinities of tryptamine analogues.” This early work investigates the binding affinities of tryptamine analogues to serotonin receptors, offering valuable data on their pharmacological properties.
- Halberstadt AL, Geyer MA (September 2011). “Multiple receptors contribute to the behavioral effects of indoleamine hallucinogens.” This study explores the multiple receptors involved in the behavioral effects of indoleamine hallucinogens, contributing to our understanding of their mechanisms.
- Gessner PK, Godse DD, Krull AH, McMullan JM (March 1968). “Structure-activity relationships among 5-methoxy-n:n-dimethyltryptamine, 4-hydroxy-n:n-dimethyltryptamine (psilocin) and other substituted tryptamines.” This research examines the structure-activity relationships of various substituted tryptamines, including psilocin, providing insights into their chemical properties.
- Lyon RA, Titeler M, Seggel MR, Glennon RA (January 1988). “Indolealkylamine analogs share 5-HT2 binding characteristics with phenylalkylamine hallucinogens.” This study investigates the binding characteristics of indolealkylamine analogs to 5-HT2 receptors, drawing comparisons with phenylalkylamine hallucinogens.
- Blough BE, Landavazo A, Decker AM, Partilla JS, Baumann MH, Rothman RB (October 2014). “Interaction of psychoactive tryptamines with biogenic amine transporters and serotonin receptor subtypes.” This research explores the interactions between psychoactive tryptamines and biogenic amine transporters as well as various serotonin receptor subtypes, enhancing our understanding of their mechanisms of action.